☆ 学会別報告(クリックすると演題の詳細が参照できます ☆
******************************************************************************************************
☆第86回日本血液学会学術集会 (2024/11/11-13) 口説5演題
☆第85回日本血液学会学術集会 (2023/10/13-15) 口説6演題
☆第83回日本血液学会学術集会 (2021/09/23-25) 口説2演題
☆第82回日本血液学会学術集会(2020/10/10-11/8) 口説3演題
☆第81回日本血液学会学術集会 (2019/10/11-13) 口説3演題
☆第80回日本血液学会学術集会 (2018/10/12-14)口説2演題, 図説1演題
☆第79回日本血液学会学術集会 (2017/10/20-22)口説3演題, 図説3演題
☆ 22nd Congress of European Hematology Association (EHA) (2017/06/22-25) 図説2演題
☆ American Society of Hematology (ASH) 2016 Annual Meeting (2016/12/03-06) 図説1演題
口説24題、図説7題 2024/12/01 update
******************************************************************************************************
★ 第86回日本血液学会学術集会 (2024/11/11-13) ★
★ O1-17C-6
Novel parameters for predicting optimal response in CML treatment
○ Kohjin Suzuki, Tomoiku Takaku, Naoki Watanabe, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Eisaku Iwanaga, Yuta Kimura, Maho Ishikawa, Hitomi Nakayama, Eriko Sato, Takayuki Tabayashi Toru Mitsumori, Tomonori Nakazato, Michihide Tokuhira, Hiroyuki Fujita, Miki Ando, Yoshihiro Hatta, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
In the treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML), achieving a major molecular response (MMR) within 12 months from the treatment initiation is considered an optimal response (OR) according to the ELN 2020 guide- lines. However, at present, there is no tool for predicting OR and therefore we aimed to identify parameters that could predict OR.535 CML patients registered in the CML Cooperative Study Group (CML-CSG) database be- tween April 2001 to September 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were divided into two groups: those who achieved MMR within 12 months of treatment initiation (OR group; n=355), and those after 13 months (non-OR group; n=180). Upon comparing the blood test data at diagnosis, our re- sults showed that the non-OR group had significantly higher white blood cell (WBC) count and eosinophil percentage/count, whereas the platelet count was significantly lower. Logistic regression analysis identified these WBC count, platelet count, and eosinophil percentage at diagnosis as significant predictors of OR. The OR group showed a significantly higher rate of MR4.5 achievement in a shorter time compared to that of the non-OR group. Our study suggests that WBC count, platelet count, and eosinophil percentage are important parameters for predicting OR. The development of a new risk score containing these parameters may enable easier prediction of OR.
The development of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) has improved the outcomes for patients (pts) with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Regarding additional chromosomal abnormalities (ACAs), we previously reported that second-generation (2G)-TKIs result in the preferred result among pts with the CML-chronic phase (CP) harboring ACAs at diagnosis.
慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)の治療では、治療開始から12ヶ月以内に主要分子応答(MMR)を達成することが、ELN 2020ガイドラインによると最適応答(OR)とみなされる。しかし、現時点ではORを予測するツールはないため、ORを予測できるパラメータを特定することを目的とした。2001年4月から2022年9月までにCML共同研究グループ(CML-CSG)データベースに登録されたCML患者535人をレトロスペクティブに解析した。患者は、治療開始後12ヶ月以内にMMRを達成した患者(OR群、n=355)と、13ヶ月以降に達成した患者(非OR群、n=180)の2つのグループに分けられた。診断時の血液検査データを比較したところ、非OR群では白血球(WBC)数および好酸球の割合/数が有意に高く、一方、血小板数は有意に低いことがわかった。ロジスティック回帰分析により、診断時の白血球数、血小板数、および好酸球率がORの有意な予測因子であることが判明した。OR群では、非OR群と比較して、MR4.5達成率が有意に高く、達成までの期間も短かった。本研究により、白血球数、血小板数、および好酸球率がORの予測に重要なパラメータであることが示唆された。これらのパラメータを含む新たなリスクスコアを開発することで、ORの予測がより容易になる可能性がある。
★ O1-17D-1
Real-world data of ponatinib administration among the patients with CML-CP based on CML-CSG database
○ Masahiro Akimoto, Michihide Tokuhira Eisaku Iwanaga, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Yuta Kimura, Naoki Watanabe, Maho Ishikawa, Hitomi Nakayama, Tomonori Nakazato, Eriko Sato,Takayuki Tabayashi, Toru Mitsumori, Tomoiku Takaku, Hiroyuki Fujita, Miki Ando, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] Although the prognosis of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) has improved remarkably after tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) era, factors such as re- sistance and intolerance still influence the outcome. In this study, we retrospectively analyzed 24 patients with CML- chronic phase (CP) who received ponatinib (Pona) based on the CML-CSG database.
[Methods] We analyzed the efficacy and safety of Pona in 24 patients.
[Results] The median age was 49 years, and the median follow-up duration was 27 months. One-third of the patients received Pona as a second-line therapy. 79.2% and 11.8% of patients were initiated at 15 mg/day and 30 mg/day, respectively. The reasons for switching to Pona were 33.3% resistance, 37.5% of adverse events (AEs), and 29.2% more efficacy. All patients survived with 87.5% of 2-y event free survival. 45.8% of all patients improved responses. Thirteen (54%) patients contin- ued Pona, whereas 11 (46%) changed or stopped due to AEs (33.3%), self-interruption (8.3%) or progressive disease (4.2%). Comparing 15 mg/day-group (15mg-G) and 30 mg/day-group (30mg-G), the ratio of MR 4.5 increased especially for 15mg-G.
[Conclusion] Based on our CML-CSG database, Pona administration showed simi- lar or greater effectiveness compared to the data of a previous pivotal study. However, the continuation ratio of 2-y was less than 50%, the ratio of MR 4.5 and the deep- er response was 29.2%. Further investigation to continue Pona and obtain a better response is required.
[背景]慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)の予後は、チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(TKI)の時代になって著しく改善されたが、再耐性や不耐性などの因子が依然として予後に影響を及ぼしている。本研究では,CML-CSGデータベースに基づき,ポナチニブ(Pona)を投与されたCML-慢性期(CP)患者24例をレトロスペクティブに解析した。
[方法]24例のPonaの有効性と安全性を解析した。
[結果] 年齢中央値は49歳で、追跡期間中央値は27ヵ月であった。患者の3分の1が二次治療としてPonaを受けた。79.2%と11.8%の患者が、それぞれ15mg/日と30mg/日で投与を開始した。Ponaへの切り替え理由は、耐性33.3%、有害事象(AE)37.5%、有効性29.2%であった。全例が生存し、2年間の無イベント生存率は87.5%であった。全患者の45.8%が奏効を改善した。13人(54%)の患者がPonaを継続したが、11人(46%)は有害事象(33.3%)、自己中断(8.3%)、進行性疾患(4.2%)により変更または中止した。15mg/日群(15mg-G)と30mg/日群(30mg-G)を比較すると、特に15mg-GでMR4.5の比率が増加した。
[結論]我々のCML-CSGデータベースに基づくと、Pona投与は以前のピボタル試験のデータと比較して同等以上の有効性を示した。しかし、2年継続率は50%未満、MR比は4.5、深部奏効率は29.2%であった。Ponaを継続投与し、よりよい効果を得るためには、さらなる検討が必要である。
★ O3-16B-1
Outcomes of chronic myeloid leukemia patients with impaired renal function
○ Eisaku Iwanaga, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Yuta Kimura, Naoki Watanabe, Maho Ishikawa, Hitomi Nakayama, Tomonori Nakazato, Eriko Sato, Takayuki Tabayashi, Toru Mitsumori, Tomoiku Takaku, Michihide Tokuhira, Masahiro Akimoto, Hiroyuki Fujita, Miki Ando, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] Multiple tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are available as first-line ther- apy for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). The choice of TKI depends on the pa- tient’s comorbidity, such as age and organ dysfunction, and aims for a better long- term outcome. The impact of renal function at diagnosis is of clinical concern regarding TKI selection.
[Methods] We retrospectively analyzed the data of patients with CML in the chronic phase who were extracted from the CML Cooperative Study Group database. A total of 602 CML cases were divided into three groups according to the chronic kidney disease (CKD) criteria: group A (eGFR >=60: CKD G1/G2, n=504), group B (eGFR 45-59: CKD G3a, n=71), group C (eGFR=< 44: CKD G3b/G4/G5, n=27).
[Results] OS and EFS were significantly worse in the renal failure group in the total cohort (10-year OS: 92% vs. 83% vs. 50%, 10-year EFS: 85% vs. 71% vs. 41%, 10- year PFS: 91% vs 83% vs 50%; p<0.001, group A, B, C, respectively). The trend was the same in patients who started with second-generation TKI (10-year OS: 90% vs. 81% vs. 72%, 10-year EFS: 82% vs. 62% vs. 52%, 10-year PFS: 90% vs. 81% vs. 72%; p<0.001). The deep molecular response rates did not significantly differ among the three groups. [Conclusion] Our data support that baseline renal failure is associated with a worse prognosis, but the deep molecular response rates are comparable in CML patients. A future study will address the choice of TKI to balance the outcome and treatment response of CML with renal impairment.
[背景]慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)の第一選択薬として、複数のチロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(TKI)が使用可能である。TKIの選択は、患者の年齢や臓器機能障害などの併存疾患によって異なり、より良好な長期転帰を目指す。診断時の腎機能の影響は、TKIの選択に関して臨床的に重要である。
[方法]CML Cooperative Study Groupのデータベースから抽出した慢性期のCML患者のデータをレトロスペクティブに解析した。合計602例のCML症例を慢性腎臓病(CKD)基準に従って3群に分けた:A群(eGFR >=60:CKD G1/G2、n=504)、B群(eGFR 45-59:CKD G3a、n=71)、C群(eGFR=< 44:CKD G3b/G4/G5、n=27)。
[結果] 全コホートにおいて、OSおよびEFSは腎不全群で有意に不良であった(10年OS: 10年OS:92%対83%対50%、10年EFS:85%対71%対41%、10年PFS:91%対83%対50%、p<0.001、それぞれA群、B群、C群)。この傾向は第2世代TKIで治療を開始した患者においても同様であった(10年OS:90% vs. 81% vs. 41%: 10年OS:90%対81%対72%、10年EFS:82%対62%対52%、10年PFS:90%対81%対72%;p<0.001)。深部分子奏効率は3群間で有意差はなかった。
[結論] 我々のデータは、ベースラインの腎不全が予後不良と関連することを支持するが、CML患者において深部分子奏効率は同等である。今後の研究では、腎障害を有するCMLの予後と治療効果のバランスをとるためのTKIの選択に取り組む予定である。
★O3-16B-4
Analysis of very elderly patients (=>75 years) with ND-CML-CP who received TKIs
○ Michihide Tokuhira, Yuta Kimura, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Naoki Watanabe, Maho Ishikawa, Hitomi Nakayama, Tomonori Nakazato, Eriko Sato, Takayuki Tabayashi, Toru Mitsumori, Masahiro Akimoto, Hiroyuki Fujita, Tomoiku Takaku, Miki Ando, Eisaku Iwanaga, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] We previously reported an analysis of elderly patients (=>65 years) with CML-CP who were treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Recent atten- tion has been paid to very elder patients aged =>75 years (VE-G). This study ana- lyzed the patients with CML-CP in VE-G to investigate sufficient TKI treatment based on in the CML-CSG database.
[Patients and Results] We analyzed 66 TKI-initiated patients with CML-CP in VE-G. The median age was 77 years, and the observation duration was 66.4 months. One- third of patients initiated with imatinib (IM), dasatinib (Das), and nilotinib (Nilo), and 60% of all patients started the reduced dose. In terms of the comparison between VE-G and younger group (Y-G, < 75 years), WBC counts in the peripheral blood of the VE-G were significantly lower than those of the Y-G (p < 0.001). The overall survival (OS) of the VE-G was significantly poorer. In VE-G, patients’ background and OS were not significantly different among 3 initiated TKIs. 82% of the VE-G received a reduced TKI dose as the final dose. One and two patients died due to AP/BP in the IM and Das, respectively. Secondary malignancies and heart failure were the other major causes of death in 5 and 3 patients, respectively. Second- generation (2-G) TKIs (Dasa and Nilo) showed a superior response compared to IM until 24 months after TKI initiation. Two (one with IM and one with Dasa) stopped TKI therapy as an attempt.
[Conclusion] Overall, although efficacy of 2-G TKIs showed superior efficacy, any initiated TKI may be acceptable for VE-G with CML-CP based on our database.
[背景]我々は以前、チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(TKI)による治療を受けたCML-CPの高齢患者(65歳以上)の解析を報告した。最近、75歳以上の超高齢患者(VE-G)に注目が集まっている。本研究では、CML-CSGデータベースに基づき、VE-GのCML-CP患者を解析し、十分なTKI治療を検討した。
[患者と結果]我々は、VE-G の CML-CP 患者 66 例を解析した。年齢中央値は 77 歳、観察期間は 66.4 ヵ月であった。3分の1の患者がイマチニブ(IM)、ダサチニブ(Das)、ニロチニブ(Nilo)で開始し、全患者の60%が減量投与を開始した。VE-Gと若年群(Y-G、75歳未満)の比較では、VE-Gの末梢血のWBC数はY-Gより有意に低かった(p<0.001)。VE-Gの全生存期間(OS)は有意に不良であった。VE-Gでは、患者背景とOSは3つの開始TKIで有意差はなかった。VE-G の 82%は最終用量として TKI の減量を受けた。IM 群と Das 群でそれぞれ 1 例と 2 例が AP/BP により死亡した。その他の主な死因は二次悪性腫瘍と心不全で、それぞれ5例と3例であった。第二世代(2-G)TKI(DasaとNilo)は、TKI開始24ヵ月後までIMと比較して優れた効果を示した。2例(IMを1例、Dasaを1例)がTKI治療を中断した。
[結論] 全体として、2-G系TKIの有効性は優れていたが、我々のデータベースによれば、CML-CPのVE-Gに対しては、どのようなTKIを開始してもよい可能性がある。
★O3-16B-5
Improvement of diabetes mellitus by dasatinib in patients with CML: a report from CML-CSG
○ Toru Mitsumori, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Tomonori Nakazato, Naoki Watanabe, Tomoiku Takaku, Maho Ishikawa, Hiroyuki Fujita, Eisaku Iwanaga, Michihide Tokuhira, Eriko Sato, Takayuki Tabayashi, Yuta Kimura, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] It is known that some TKIs, such as nilotinib and ponatinib, can cause diabetes mellitus (DM) exacerbation. However, the effect of dasatinib on DM is inconsistent. In this study, we investigated the effect of dasatinib on DM in patients with CML in a retrospective manner by using the CML Co- operative Study Group (CML-CSG) database. [Methods] Patients with CML concomitantly having DM were extracted, and those available at the HbA1c level at diagnosis and any of the 3, 6, 9, or 12 months after TKI therapy were analyzed. Patients who started DM therapy at starting TKI were excluded.
[Results] Seventeen patients were initially treated with dasatinib. All were in the chronic phase; the median age was 64.5 years, 4 were women, and the median HbA1c level at diagnosis was 7.15% (range 5.8-9.4). Compared to the HbA1c levels at diagnosis, those were significantly improved at three months (median 7.35% to 6.7% in 10 paired; p = 0.0067), at six months (median 7.1% to 6.3% in 14 paired; p = 0.00002), at nine months (median 7.2% to 6.4% in 11 paired; p = 0.002), and at 12 months (median 7.1% to 6.3% in 17 paired; p = 0.023).
[Discussion] Dasatinib is known to inhibit SRC family kinases, which are involved in insulin secretion, insulin resistance, and glucose metabolism. Although this study demonstrates the improvement of DM by dasatinib, further studies are needed to elucidate the effect of this drug on glucose metabolism.
[背景]ニロチニブやポナチニブなどの一部のTKIは糖尿病(DM)の増悪を引き起こすことが知られている。しかし、ダサチニブのDMに対する効果は一貫していない。本研究では、CML Co-operative Study Group(CML-CSG)のデータベースを用いて、CML患者におけるダサチニブのDMに対する影響をレトロスペクティブに検討した。
[方法]DMを合併したCML患者を抽出し、診断時およびTKI治療後3、6、9、12ヶ月のいずれかのHbA1c値が得られた患者を解析した。TKI治療開始時にDM治療を開始した患者は除外した。
[結果]7例の患者がダサチニブによる初回治療を受けた。年齢中央値は64.5歳、女性4人、診断時のHbA1c値中央値は7.15%(範囲5.8-9.4)であった。診断時のHbA1c値と比較して、3ヵ月後(中央値7.35%→6.7%、ペア10人、p=0.0067)、6ヵ月後(中央値7.1%→6.3%、ペア14人、p=0.00002)、9ヵ月後(中央値7.2%→6.4%、ペア11人、p=0.002)、12ヵ月後(中央値7.1%→6.3%、ペア17人、p=0.023)に有意に改善した。
[結論] ダサチニブは、インスリン分泌、インスリン抵抗性、グルコース代謝に関与するSRCファミリーキナーゼを阻害することが知られている。本研究はダサチニブによるDMの改善を証明するものであるが、糖代謝に対するこの薬剤の効果を解明するためにはさらなる研究が必要である。
★ 第85回日本血液学会学術集会 (2023/10/13-15) ★
★ O1-pm2-8#1
Analysis of CML patients with additional chromosomal abnormalities based on CML-CSG database
○Yuta Kimura, Michihide Tokuhira, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Naoki Watanabe, Maho Ishikawa,Hitomi Nakayama, Tomonori Nakazato,Eriko Sato, Takayuki Tabayash, Toru Mitsumori, Tomoiku Takaku, Hiroyuki Fujita, Eisaku Iwanaga, Miki Ando, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] The development of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) has improved the outcomes for patients (pts) with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Regarding additional chromosomal abnormalities (ACAs), we previously reported that second-generation (2G)-TKIs result in the preferred result among pts with the CML-chronic phase (CP) harboring ACAs at diagnosis.
[Results] Of the 585 eligible pts with ade- quate karyotype analysis, 522 had sole t (9;22)(q34;q11) (Ph1), while 63 had ACAs, including 15 major (M-) and 48 minor (m-) routes (r). Risk factor such as age was not significantly different between the two groups. Regarding responses, including the accumulative major molecular response (MMR) and MR4.5 ratios, no significant differences were detected between the two groups. However, the transformation-free survival of ACA+ was significantly lower than that of ACA-. Among the ACA+ group, imatinib initiation showed a significantly lower accumula- tive MR4.5 ratio than 2G-TKIs. In addition, m-r indicated inferior responses com- pared to M-r, although without a significant difference, and the transformation-free survival of m-r was significantly lower than that of M-r (p=0.0318). In terms of ACA numbers, except for Ph1, 35 pts indicated one ACA, and a 3-way translocation was most frequently observed in 13 pts in m-r. -Y was detected in 4 pts of m-r, and the cumulative MMR was relatively low even under 2G-TKI initiation with one pt develop- ing transformation.
[Conclusion] Our retrospective study revealed unique clinical features of ACA+ in pts with CML-CP and suggested a TKI strategy.
[背景]チロシンキナーゼ阻害剤 (TKI) の開発により、慢性骨髄性白血病 (CML) 患者の予後は改善されてきた。付加的染色体異常(ACA)に関して、我々は以前に、診断時にACAを有するCML-慢性期 (CP) 患者において、第2世代 (2G) -TKIが好ましい結果をもたらすことを報告した。
[結果]585例の適格患者のうち、522例が単独でt(9;22)(q34;q11)(Ph1)を有していた。63例がACAを有し、そのうち15例がメジャー(M-)、48例がマイナー(m-)ルート(r)であった。 年齢など背景因子は両群間に有意差はなかった。累積主要分子反応(MMR)およびMR4.5比を含む反応において、両群間に有意差は検出されなかった。しかし、ACA+群の無急性転化率はACA-群より有意に低かった。ACA+群では、イマチニブ投与開始時の蓄積MR4.5率は2G-TKI群より有意に低かった。また、m-rはM-rと比較し、有意差はないものの奏効率で劣り、m-rの無急性転化率はM-rより有意に低かった (p=0.0318) 。ACA数では、Ph1を除き35例に1個のACAが認められ、m-rでは13例に3-way転座が最も多く認められた。m-rでは4例に-Yが検出され、2G-TKI投与下でも累積MMRは比較的低く、1例に急性転化を認めた。
[結論]我々の後方視的研究は、CML-CP患者におけるACA+のユニークな臨床的特徴を明らかにし、TKI戦略に示唆した。
★ O1-pm2-8#2
Second malignancies in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors
○Hitomi Nakayama, Tomonori Nakazato, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Yuta Kimura, Naoki Watanabe, Maho Ishikawa, Eriko Sato, Takayuki Tabayashi, Toru Mitsumori, Tomoiku Takaku, Michihide Tokuhira, Hiroyuki Fujita, Miki Ando, Eisaku Iwanaga, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] As tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have dramatically improved the sur- vival of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), long-term outcomes such as second primary malignancies (SPMs) have become an increasingly relevant con- cern for CML survivors. In this retrospective study, we evaluated the incidence of SPMs in CML patients treated with imatinib, dasatinib, and nilotinib.
[Methods] Data from 590 patients who were extracted from the CML Cooperative Study Group database was analayzed. The duration of each TKI administration for individual patient was investigated. Patients were grouped by TKI with the longest duration of exposure. SPM risk was accessed by cumulative incidence and stan- dardized incidence ratios (SIR).
[Results] Of the 590 patients followed for 4692.9 person-years, 39 (6.6%) developed SPMs. The 5-year cumulative incidence of SPMs for patients treated with imatinib, dasatinib, and nilotinib was 3.3% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.4-6.7%), 7.1% (95% CI: 4.0-11.4%) and 1.2% (95% CI: 0.2-4.0%), respectively (P = 0.03). The SIR of overall cohort was 1.09 (95% CI: 0.75-1.43). On subgroup analyses, com- pared to the age and sex matched general population, elevated risk was observed for male patients treated with dasatinib (SIR = 2.12, 95% CI: 1.05-3.19).
[Conclusions] tion. However, in our cohort, an increased risk was observed in male patients treated with dasatinib, suggesting that careful observation and monitoring may be needed in these patients.
[背景]チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬 (TKI) が慢性骨髄性白血病 (CML) 患者の劇的な生存率の改善に伴い、二次原発悪性腫瘍(SPM)などの長期転帰は、CML生存者にとってますます重要な問題となっている。この後方視的研究では、イマチニブ、ダサチニブ、ニロチニブによる治療を受けたCML患者におけるSPMの発生率を評価した。
[方法] CML Cooperative Study Groupのデータベースから抽出した590例のデータを解析した。個々の患者のTKI投与期間を調査し、投与期間が最も長いTKIで患者をグループ分けした。SPMリスクは累積罹患率および標準化罹患率比(SIR)により算出した。
[結果] 4692.9人年追跡した590人の患者のうち、39人(6.6%) がSPMを発症した。イマチニブ、ダサチニブ、ニロチニブによる治療を受けた患者におけるSPMの5年累積発生率は、それぞれ3.3% (95%信頼区間[CI]:1.4-6.7%) 、7.1% (95%CI:4.0-11.4%) 、1.2% (95%CI:0.2-4.0%) であった (P = 0.03) 。コホート全体のSIRは1.09 (95%CI:0.75-1.43)であった。年齢と性別をマッチさせた一般集団と比較したサブグループ解析では、ダサチニブ治療を受けた男性患者でリスクの上昇が観察された (SIR = 2.12、95%CI: 1.05-3.19) 。
[結論] TKI治療を受けたCML患者におけるSPMの全発生率は、一般集団と同等であった。しかし、本コホートでは、ダサチニブ治療を受けた男性患者においてリスクの上昇が認められ、これらの患者では注意深い観察とモニタリングが必要であることが示唆された。
★ O2-pm1-11#1
Pregnancy and childbirth in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in real-life practice
○Eriko Sato, Eisaku Iwanaga, Maho Ishikawa, Tomoiku Takaku, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Takayuki Tabayashi, Yuta Kimura, Michihide Tokuhira, Naoki Watanabe, Toru Mitsumori, Tomonori Nakazato, Hitomi Nakayama, Hiroyuki Fujita, Miki Ando, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[BACKGROUND] Tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), the 1st line treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), have known teratogenic potential, however, the effects of TKIs on fertility are not yet fully understood. CML also affects women and men of childbearing age, the position of pregnancy (PG) during treatment is very important in the life plan, though less known about real-life data.
[METHODS] Of the 626 pa- tients enrolled in the CML-CSG, we retrospectively analyzed the cases that led to
[RESULTS] There were 57 women of possible fertility who were under 40 years of age at onset. Of these, 7 patients became PG, with a total of 14 PG cases; median age of CML diagnosis was 23.0 (18-33) years, median PG age was 30.5 (22-38) years and median time from onset to conception was 7.5 (2-13) years. At the time of PG discovery, 6 cases were treated with interferon (IFN), 8 with any TKIs. One dasatinib (DS) and 1 nilotinib (NL) cases elected abortion. Of 12 cases with willing to continue PG, 7 cases had normal live infant: 4 out of seven treated with IFN, 3 with DS, subsequently, 1 UN. Three patients treated with DS, 1 stop treatment, 1 changed to IFN, and 1 changed to IFN during 1st trimester then resumed TKI. One spontaneous abortion with IFN, 1 with NL and 1 with DS. One stillbirth on IFN. Hy- pertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) occurred 6 out of 14 PG cases. Two men on TKIs treatment who wish to have a baby successfully had child respectively.
[CONCLUSION] In this study, HDP occurred higher than general PG. Accumulation of clinical fertility data both women and men are required.
[背景] 慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)の1次治療薬であるチロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(TKI)には催奇形性があることが知られているが、TKIの生殖能への影響はまだ完全には解明されていない。CMLは出産適齢期の女性や男性にも影響を及ぼすため、治療中の妊娠(PG)の位置づけはライフプラン上非常に重要であるが、実際のデータについてはあまり知られていない。
[方法] CML-CSGに登録された626例の患者のうち、PGに至った症例をレトロスペクティブに解析した。
[結果] 発症時年齢が40歳未満で妊娠可能な女性は57人であった。このうち7例がPGとなり、合計14例がPG症例であった;CML診断年齢の中央値は23.0歳(18-33歳)、PG年齢の中央値は30.5歳(22-38歳)、発症から妊娠までの期間の中央値は7.5年(2-13年)であった。PG発見時、6例はインターフェロン(IFN)、8例はいずれかのTKIで治療されていた。ダサチニブ(DS)1例とニロチニブ(NL)1例は中絶を選択した。PGを継続する意思のある12例のうち、7例が正常な生児を出産した。DS で治療した 3 例、1 例は治療中止、1 例は IFN に変更、1 例は妊娠第 1 期中に IFN に変更し、その後 TKI を再開した。IFN で自然流産 1 例、NL で 1 例、DS で 1 例。IFNで死産1例。妊娠高血圧症候群(HDP)がPG14例中6例にみられた。出産を希望するTKI治療中の男性2人はそれぞれ出産に成功した。
[結論] 本研究では、HDPは一般的なPGよりも高い頻度で発生した。女性、男性ともに不妊臨床データの蓄積が必要である。
★ O2-pm2-11#2
Outcomes of CML patients not achieving optimal response at one year of TKI treatment
○Eisaku Iwanaga, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Yuta Kimura, Naoki Watanabe, Maho Ishikawa, Hitomi Nakayama, Tomonori Nakazato, Eriko Sato, Takayuki Tabayashi, Toru Mitsumori, Tomoiku Takaku, Michihide Tokuhira, Hiroyuki Fujita, Miki Ando, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] In the era of second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (2G-TKIs), most patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) achieve major molecular re- sponse (MMR: BCR-ABL1 international scale: IS =< 0.1%). Guidelines adopt the achievement of 1-year MMR as the optimal milestone for long-term disease control, while IS >1% or CCyR (Complete cytogenetic response) for the failure boundary. However, it is unclear to what extent the 1-year disease status affects the CML prog- nosis in the 2G-TKI setting.
[Methods] We analyzed the data of patients with CML in the chronic phase who were extracted from the CML Cooperative Study Group database. A total of 370 CML cases started with the 2G-TKI divided into three groups according to the IS and CCyR status at one year of treatment: “optimal” (MMR+, n=271), “warning” (MMR- and IS<1% / CCyR+, n=71), “failure” (MMR- and IS>=1% / CCyR-, n=18). Overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and CML-related death (CRD) were compared between the three groups.
[Results] The prognosis of “failure” was significantly inferior to “optimal” and “warning” (10-year OS: 92.1% vs 82.5% vs 53.3%, 10-year PFS: 92.9% vs 79.3% vs 74.0%, 10-year CRD: 0.43% vs 1.5% vs 33%; p<0.001, “optimal” vs “warning” vs “failure”, re- spectively). The “failure” required the frequent >=2 lines of TKI than “optimal” or “warning” (33.5%: optimal, 52.1%: warning, 66.6%: failure).
[Conclusion] Our data indicate that “failure” patients are associated with high CRD. A future study will address the choice and switch timing of TKI to reduce the CRD of the “failure” group.
[背景] 第二世代チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(2G-TKI)の時代には、慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)患者のほとんどが主要分子生物学的奏効(MMR:BCR-ABL1国際スケール:IS =< 0.1%)を達成している。ガイドラインでは、1年MMRの達成を長期病勢コントロールの最適なマイルストーンとし、IS>1%またはCCyR(完全細胞遺伝学的奏効)を不成功の境界としている。しかし、1年後の病勢がCMLにおける2G-TKI療法にどの程度影響するかは不明である。
[方法] CML Cooperative Study Groupのデータベースから抽出した慢性期のCML患者のデータを解析した。2G-TKIを開始したCML症例370例を、治療開始1年後のISとCCyRの状態によって3群に分けた: 「至適」(MMR+、n=271)、「警告」(MMR-かつIS<1%/CCyR+、n=71)、「失敗」(MMR-かつIS>=1%/CCyR-、n=18)である。全生存期間(OS)、無増悪生存期間(PFS)、CML関連死(CRD)を3群間で比較した。
[結果] 「失敗」の予後は「至適」および「警告」に比べて有意に劣っていた(10年OS: 10年OS:92.1%対82.5%対53.3%、10年PFS:92.9%対79.3%対74.0%、10年CRD:0.43%対1.5%対33%、p<0.001、「至適」対「警告」対「失敗」)「失敗」では、「至適」または「警告」よりも第2次以降のTKIを必要とした(33.5%:「至適」、52.1%:「警告」、66.6%:「失敗」)。
[結論] 我々のデータは、”「失敗」 “患者が高いCRDと関連していることを示している。今後の研究では、”「失敗」 “群のCRDを減少させるためのTKIの選択と切り替えのタイミングについて検討する予定である。
★ O2-pm2-11#3
Usefulness of new risk prediction model for VAEs in Japanese patients with CML treated with TKIs
○Naoki Watanabe, Tomoiku Takaku, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Yuta Kimura, Eisaku Iwanaga, Toru Mitsumori, Maho Ishikawa, Hitomi Nakayama, Tomonori Nakazato, Hiroyuki Fujita, Eriko Sato, Takayuki Tabayashi, Michihide Tokuhira, Miki Ando, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] Vascular adverse events (VAEs) increase in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and may be fatal complications. We previously reported useful tools to predict VAEs incidence in CML patients treated with TKIs. A guideline for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease was updated by Japan Atherosclero- sis Society in 2022. However, it is unclear whether a new risk model (Hisayama score model) predicts VAEs in CML patients during TKI treatment. Herein, we investigated usefulness of the new prediction model for VAEs in CML patients.
[Methods] We retrospectively analyzed 626 CML patients in the chronic or accelerated phases enrolled in the CML Cooperative Study Group database.
[Results] 45 events in 42 (6.7%) of these patients were VAEs. At the time of VAE incidence, 13 events occurred during treatment with imatinib, 24 with nilotinib, four with dasatinib, two with bosutinib, and one with ponatinib. VAE incidence comprised 19 events of ischemic heart disease, 16 of cerebral infarction, and 10 of peripheral arterial occlusive dis- ease. The Hisayama score model in the new guideline detected most CML patients with high risk of VAEs.
[Conclusion] The new risk model may be useful tool for prediction of VAEs in CML patients during TKI treatment. VAEs risk assessment contribute to treatment optimization for CML patients treat- ed with TKIs.
[背景] チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(TKI)治療を受けた慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)患者では血管有害事象(VAE)が増加し、致命的な合併症となる可能性がある。われわれは以前、TKI治療を受けたCML患者におけるVAE発生を予測する有用なツールを報告した。動脈硬化性心血管病のガイドラインは2022年に日本動脈硬化学会によって更新された。しかし、新たなリスクモデル(Hisayama score model、久山スコアモデル)がTKI治療中のCML患者のVAEを予測するかどうかは不明である。ここでは、CML患者のVAEに対する新しい予測モデルの有用性を検討した。
[方法] CML Cooperative Study Groupデータベースに登録された慢性期または移行期のCML患者626例をレトロスペクティブに解析した。
[結果] このうち42例(6.7%)の45事象にVAEを認めた。VAE発生時、イマチニブで13件、ニロチニブで24件、ダサチニブで4件、ボスチニブで2件、ポナチニブで1件のイベントが発生した。VAE発生率は虚血性心疾患19件、脳梗塞16件、末梢動脈閉塞性疾患10件であった。新ガイドラインの久山スコアモデルを用いると、VAEリスクの高いCML患者のほとんどを検出した。
[結論 ] 新しいリスクモデルは、TKI治療中のCML患者におけるVAEを予測する有用なツールとなりうる。VAEリスク評価は、TKI治療を受けているCML患者の治療最適化に寄与する。
★ O2-pm2-11#5
The effect of introduction of 2G-TKI as first-line therapy on CML treatment modalities and outcomes
○Noriyoshi Iriyama, Eisaku Iwanaga, Yuta Kimura, Naoki Watanabe, Maho Ishikawa, Hitomi Nakayama, Eriko Sato, Takayuki Tabayashi, Toru Mitsumori, Tomoiku Takaku, Tomonori Nakazato, Michihide Tokuhira, Hiroyuki Fujita, Miki Ando, Yoshihiro Hatta, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
This study investigates the treatment modality and outcome changes of chronic myeloid leukemia in the chronic phase (CP-CML) after the approval of second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (2G-TKIs) for first-line thera- py. Patients who underwent TKI therapy up to December 2010 were includ- ed in the “imatinib era group (n = 185),” while those after January 2011 were included in the “2G-TKI era group (n = 425)”. All patients in the imati- nib era group were initially treated with imatinib, whereas patients in the 2G-TKI era group were mostly treated with dasatinib or nilotinib. However, no significant differences were observed in outcomes, including progression- free survival, overall survival, and CML-related death (CRD) between groups. When stratified by risk scores, prognostic predictability of the ELTS score was superior to that of the Sokal score. Even though both scoring sys- tems anticipated CRD in the imatinib era, only the ELTS score predicted CRD in the 2G-TKI era. Notably, the outcome of patients with a high-risk based on ELTS was favorable in the 2G-TKI era group than that in the imatinib era group. Thus, expanding the treatment options may have improved patient outcomes in CP-CML, particularly in patients with high-risk based on ELTS.
本研究は、第二世代チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(2G-TKI)が第1選択薬として承認された後の慢性期慢性骨髄性白血病(CP-CML)の治療法と転帰の変化について検討したものである。2010年12月までにTKI療法を受けた患者を「イマチニブ時代群(n=185)」、2011年1月以降の患者を「2G-TKI時代群(n=425)」とした。イマチニブ時代群では全例がイマチニブによる初期治療を受けたが、2G-TKI時代群ではほとんどがダサチニブまたはニロチニブによる治療であった。しかし、無増悪生存期間、全生存期間、CML関連死(CRD)などの転帰に群間で有意差は認められなかった。リスクスコアで層別化すると、ELTSスコアの予後予測能はSokalスコアよりも優れていた。イマチニブ時代には両スコアリングシステムともCRDを予測したが、2G-TKI時代にはELTSスコアのみがCRDを予測した。注目すべきは、ELTSに基づく高リスク患者の転帰は、イマチニブ時代よりも2G-TKI時代の方が良好であったことである。したがって、治療選択肢の拡大は、特にELTSに基づく高リスク患者において、CP-CMLの患者転帰を改善した可能性がある。
—————————————————————————————————————————
★第83回日本血液学会学術集会 (2021/09/23-09/25) ★
★ OS1-5B-2
Comparison among the patients with ND-CML-CP who received dasatinib, focusing on age
○Michihide Tokuhira, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Naoki Watanabe, Shun Tsuchiya, Tomoiku Takaku, Tomonori Nakazato, Yuta Kimura, Eriko Sato, Keiji Sugimoto, Hiroyuki Fujita, Maho Ishikawa, Eisaku Iwanaga, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background ]Although excellent efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) has been proved among the patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in the chronic phase (ND-CML-CP), influence of age has not well understood.
[Patients and Results] The analysis was performed between 61 patients aged less than 65 years (non-elder group, NE-G) and 37 patients aged 65 years and more (elder group, E-G), who received dasatinib (Das) as the first line. In the patients’ background between 2 groups, older age, shorter observation duration, higher Sokal score, and higher ELTS scor were de- tected in patients of E-G with significant differences. Regarding status at the time of final observation, 53.9% of NE-G and 40.5% of E-G continued Das as the first line. Simultaneously, the ratios of discontinuation of TKI because of various reasons of NE-G and E-G were 11.5% and 24.3%, respectively, although the ratios of second and the third lines after Das were almost simi- lar rates. Regarding efficacy, the cumulative MMR rates during Das treat- ment of NE-G and E-G at time of 6 months after initiation were 37.7% and 18.9%, respectively. Those at 12 and 24 months were 63.9% and 37.8%, re- spectively, and 78.7% and 51.4%, respectively. At each point, the significant difference was not detected. In terms of outcome, 2 patients and 6 patients died in NE-G and E-G, respectively. Five-year OS was 88.8% in NE-G and 84.6% in E-G.
[Conclusion] This retrospective study demonstrated similar efficacies regardless of age in the setting of Das administration among the patients with ND-CML-CP.
[背景]慢性期の慢性骨髄性白血病(ND-CML-CP)と新たに診断された患者において、チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(TKI)の優れた有効性が証明されているが、年齢の影響は十分に理解されていない。
[患者および結果]初期治療としてダサチニブ(Das)を投与された65歳未満の患者61人(非高齢群、NE-G)と65歳以上の患者37人(高齢群、E-G)の解析を行った。2群間の患者背景では、E-G群で高年齢、観察期間短縮、Sokalスコア高値、ELTSスコア高値が有意差をもって認められた。最終観察時の状態については、NE-G群では53.9%、E-G群では40.5%が初期治療としてDasが継続されていた。同時に、様々な理由でTKIを中止した割合は、NE-Gで11.5%、E-Gで24.3%であったが、Das後の第2次治療、第3次治療の割合はほぼ同率であった。有効性に関しては、NE-GとE-GのDas治療中の累積MMR率は、開始後6カ月でそれぞれ37.7%と18.9%であった。12ヵ月後,24ヵ月後の累積MMR率はそれぞれ63.9%,37.8%,78.7%,51.4%であった。各時点で有意差は認められなかった。転帰に関しては、NE-Gでは2例、E-Gでは6例が死亡した。5年OSはNE-Gで88.8%、E-Gで84.6%であった。
[結論]この後方視的研究では、ND-CML-CP患者において、Das投与は年齢を問わず同様の有効性を示した。
★ OS1-5B-3
Influence of age among the patients with newly diagnosed CML-CP who were treated with nilotinib
○Michihide Tokuhira, Yuta Kimura, Tomonori Nakazato, Maho Ishikawa, Keiji Sugimoto, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Shun Tsuchiya, Naoki Watanabe, Tomoiku Takaku, Hiroyuki Fujita, Eriko Sato, Eisaku Iwanaga, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background]Although excellent efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors has been proved among the patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leu- kemia in the chronic phase (ND-CML-CP), influence of age is not well ana- lyzed.
[Patients and Results] The analysis was performed between 56 patients aged less than 65 years (non-elder group, NE-G) and 24 patients aged 65 years and more (elder group, E-G), who received nilotinib (Nilo) as the first line, from the CML-CSG database. In the patients’ background between 2 groups, the older age, the shorter observation duration, higher Sokal score, and higher ELTS score were detected in patients of E-G with significant dif- ferences. Regarding status at the time of final observation, 84% of NE-G and 61% of E-G continued Nilo as the first line. Simultaneously, the ratios of dis- continuation of tyrosine kinase inhibitor of NE-G and E-G were 7.1% and 17.4%, respectively. Regarding efficacy, the cumulative MMR rates of NE-G and E-G during Nilo treatment at time of 6 months after initiation were 42.9% and 45.8%, respectively, without a significant difference (p=1). Similarly, those at 12 months and 24 months, the ratios were 71.4% and 75%, respectively (p=1), and 80.4% and 79.2%, respectively (p=1). In terms of overall survival, there was no significant difference between 2 groups (p=0.386). Five-year OS was 98.1% in NE-G and 93.3% in E-G.
[Conclusion] This retrospective study demonstrated similar efficacies regardless of age in the setting of Nilo administration among the patients with ND- CML- CP.
[背景]慢性期の慢性骨髄性白血病(ND-CML-CP)と新たに診断された患者において、チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬の優れた有効性が証明されているが、年齢の影響は十分に解析されていない。
[患者と結果]CML-CSGのデータベースから、初期治療としてニロチニブ(Nilo)を投与された65歳未満の患者56例(非高齢群、NE-G)と65歳以上の患者24例(高齢群、E-G)を解析した。両群の患者背景を比較すると、E-G群では年齢が高いこと、観察期間が短いこと、Sokal scoreが高いこと、ELTS scoreが高いことが有意差をもって検出された。最終観察時の状態については、NE-G群では84%、E-G群では61%がファーストラインとしてニロを継続していた。同時に、NE-GとE-Gのチロシンキナーゼ阻害薬の継続中止率は、それぞれ7.1%と17.4%であった。有効性については、Nilo投与開始6ヵ月後の累積MMR率はNE-Gが42.9%、E-Gが45.8%であり、有意差はなかった(p=1)。同様に12ヵ月後、24ヵ月後においてもそれぞれ71.4%、75%(p=1)、80.4%、79.2%(p=1)であった。全生存期間に関しては、2群間に有意差はなかった(p=0.386)。5年OSはNE-G群で98.1%、E-G群で93.3%であった。
[結論]この後方視的研究では、ND-CML-CP患者において、Niloは投与時の年齢に関係なく同様の有効性が示された。
————————————————————————————————————————-
★ 第82回日本血液学会学術集会(2020/10/10-11/8) ★
★ OS-22-5
Clinical results of dasatinib treatment in elderly patients with newly diagnosed CML-CP
○Michihide Tokuhira, Yuta Kimura, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Shun Tsuchiya, Tomoiku Takaku, Yuriko Fujita, Tomonori Nakazato, Eriko Sato, Keiji Sugimoto, Hiroyuki Fujita, Maho Ishikawa, Isao Fujioka, Yoshihiro Hatta, Norio Komatsu, Norio Asou, Masahiro Kizaki, Eisaku Iwanaga, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] Although several recent clinical studies suggest that dose modification of dasatinib (Das) is an attractive strategy to obtain a better balance between efficacy and safe- ty, the proper usage of Das in elderly patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in the chronic phase (CP) has not been well established.
[Patients and Results] This study analyzed 38 patients aged >=65 years who had newly diagnosed (ND) -CML-CP and were treated with Das as the initial therapy from the CML CSG data- base. These patients had a median age of 73 years. Eighty-eight percent of the 34 patients with over a year of tyrosine kinase inhibitor administration achieved MMR, with a median duration of Das administration of 6 months. Two groups were identi- fied based on the initial Das dose: 100 mg/day (standard group [S-G], N=26) and <100 mg/day (reduced group [R-G], N=12). The proportions of MMR after a year of treatment in the corresponding groups were 73% and 50%, respectively, indicating the superior efficacy in the S-G. However, 92% of patients in the S-G required dose reduction, resulting in a median final dose of 50 mg/day. The median duration of 100 mg/day administration in the S-G was 6 months; the Das dose was reduced to <100 mg/day within 3 months of Das initiation in 42% of patients in the S-G.
[Conclusion] Although this analysis supported the superior efficacy of a standard Das dose (100 mg/day), a reduced starting dose, such as 50 mg/day, or prompt dose reduction within a couple of months after initiation at 100 mg/day may be an attractive strategy for elderly patients with CML-CP.
[背景]最近のいくつかの臨床研究から、ダサチニブ(Das)の用量変更は有効性と安全性のより良いバランスを得るための魅力的な戦略であることが示唆されているが、慢性期(CP)の慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)の高齢患者におけるDasの適切な使用法は十分に確立されていない。
[患者と結果]本研究では、CML CSGデータベースから、新規診断(ND)-CML-CPで、初回治療としてDasによる治療を受けた65歳以上の患者38人を分析した。これらの患者の年齢中央値は73歳であった。チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬投与期間が1年以上であった34例のうち88%がMMRを達成し、Das投与期間の中央値は6ヵ月であった。最初のDas投与量に基づいて2群に分類した:100mg/日(標準群[S-G]、N=26)と100mg/日未満(減量群[R-G]、N=12)。投与1年後のMMR割合はそれぞれ73%、50%であり、S-G群の有効性が優れていることが示された。しかし、S-G群では92%の患者が減量を必要とし、その結果、最終投与量の中央値は50mg/日となった。S-Gにおける100mg/日の投与期間中央値は6ヵ月であった;S-Gの患者の42%において、Das投与開始後3ヵ月以内にDas投与量は100mg/日未満に減少されていた。
[結論]この解析では、標準的なDas用量(100mg/日)の優れた有効性が支持されたが、高齢のCML-CP患者にとっては、開始用量を50mg/日など減量するか、100mg/日で開始後2~3ヵ月以内に速やかに減量することが魅力的な戦略と考えられた。
★ OS-22-6
Clinical results of nilotinib treatment in elderly patients with newly diagnosed CML-CP
○Michihide Tokuhira, Yuta Kimura, Yuriko Fujita, Tomonori Nakazato, Maho Ishikawa, Keiji Sugimoto, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Shun Tsuchiya, Tomoiku Takaku, Hiroyuki Fujita, Eriko Sato, Isao Fujioka, Norio Asou, Yoshihiro Hatta, Norio Komatsu, Masahiro Kizaki, Eisaku Iwanaga, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] Recent attention has been paid to clinical adjustment of the dose of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) to balance efficacy and safety in patients with chronic myeloid leu- kemia (CML) in the chronic phase (CP). As the proper use of TKIs in elderly pa- tients with CML-CP is not well established, we retrospectively analyzed the clinical results of nilotinib (Nilo) treatment in elderly patients with newly diagnosed (ND)-CML-CP.
[Patients and Results] This study analyzed 22 patients aged >=65 years who had ND-CML-CP and were treated with Nilo as the initial therapy from the CML-CSG database. A median ob- served duration was 32 months and a median age was 74 years. Eighty percent of patients continued Nilo administration. Twenty-one patients (86%) achieved MMR following a median of 6 months of Nilo administration. No patient progressed to the accelerated or blast phase. There were two groups defined based on the initial dose of Nilo: 600 mg/day Nilo (standard group [S-G]) and 300 mg/day Nilo (reduced group [R-G]). The ratios of MMR by year were 85% and 88% in S-G and R-G during Nilo administration, respectively. Seven and three patients developed adverse events in each group, respectively. Although five patients in the S-G (38%) had a reduction in the Nilo dose due to AEs, no patient was administered R-G.
[Conclusion] This retrospective study demonstrated the excellent outcomes of Nilo administration in elderly patients with CML-CP. Dose reduction of Nilo in elderly patients is an at- tractive management strategy.
[背景]近年、慢性期の慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)患者における有効性と安全性のバランスを考慮したチロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(TKI)の用量調節が注目されている。高齢のCML-CP患者におけるTKIの適切な使用法は確立されていないため、我々は高齢の新規診断(ND)-CML-CP患者におけるニロチニブ(Nilo)治療の臨床成績を後方視的に解析した。
[患者と結果]本研究では、CML-CSGデータベースから、ND-CML-CPを発症し、初回治療としてNiloによる治療を受けた65歳以上の患者22例を解析した。投与期間中央値は32ヵ月、年齢中央値は74歳であった。患者の80%がNilo投与を継続していた。21例(86%)がMMRを達成し、中央値は6ヵ月であった。加速期または芽球期に進行した患者はいなかった。Niloの初回投与量に基づいて、600mg/日のNilo(標準群[S-G])と300mg/日のNilo(減量群[R-G])の2群を定義した。Nilo投与中の投与後1年次におけるMMR比率は、S-G群で85%、R-G群で88%であった。有害事象 (AE) は各群でそれぞれ7例と3例に発現した。S-G群では5例(38%)がAEにより減量されていたが、R-G群ではなかった。
[結論]この後方視的研究は、高齢のCML-CP患者におけるNilo投与の優れた結果を実証した。高齢患者におけるNiloの減量は、有効な管理戦略である。
★ OS-24-2
Risk factors and management of pleural effusion in the dasatinib treated Japanese CML patients
○Shun Tsuchiya, Tomoiku Takaku, Isao Fujioka, Naoki Watanabe, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Eriko Sato, Tomonori Nakazato, Yuta Kimura, Keiji Sugimoto, Hiroyuki Fujita, Maho Ishikawa, Eisaku Iwanaga, Yoshihiro Hatta, Norio Asou, Masahiro Kizaki, Norio Komatsu, Michihide Tokuhira, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background]The development of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) has dramatically improved outcomes in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). However, due to prolonged treatment durations, the management of various adverse events (AEs) has become time-consuming. Pleural effusion (PE) is one of the frequent AE of dasatinib, especially in elderly patients. However, the clinical aspects of PE in Japa- nese patients with CML in real-world clinical practice is limited.
[Patients and Results] This study analyzed 15 risk factors for PE based on previous reports, management of PE, and treatment response in 89 patients with chronic phase CML of the 396 pa- tients identified from the CML-CSG database who were treated with dasatinib as the initial therapy . PE occurred in 44 (49%) of 89 patients. Five factors (age, diabetes, renal dysfunction, hypertension, and history of heart disease) in univariate analysis and 1 factor (age ) in multivariate analysis were identified as significant risk factors for PE. The most popular management was dasatinib dose reduction and the addi- tion of a diuretic. We also found that the deep molecular response rate was similar in patients with and without a PE.
[Discussion and Conclusion] This retrospective study revealed several risk factors for the development of PE in Japanese patients. Fur- ther, it revealed that treatment response was not related to a better clinical response. The identified novel risk factors and management of PE based on the analyzed data obtained from real-world settings are valuable for clinicians.
[背景】チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(TKI)の開発により、慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)患者の予後は劇的に改善した。 しかし、治療期間が長期化したため、様々な有害事象(AE)の管理に時間を要するようになっている。胸水貯留(PE)は、特に高齢患者において頻度の高い有害事象の1つである。しかし、実臨床における日本人のCML患者における胸水貯留の臨床的側面の解析は限られている。
[患者と結果]CML-CSG データベースから同定された 396 例の慢性期 CML 患者のうち、初回治療としてダサチニブを投与された 89 例を対象に、過去の報告に基づくPEの15の危険因子、PEの管理、治療反応性を解析した。PEは89例中 44 例(49%)に発現した。単変量解析では5因子(年齢、糖尿病、腎機能障害、高血圧、心疾患の既往)、多変量解析では 1 因子(年齢)がPEの有意なリスク因子として同定された。最も一般的な管理法は、ダサチニブの減量と利尿薬の追加であった。また、深部分子奏効率はPEの有無にかかわらず同程度であった。
[考察と結論】この後方視的研究により、日本人患者におけるPE発症のいくつかの危険因子が明らかになった。さらに、治療効果は臨床効果の向上とは無関係であることが明らかになった。実際の臨床現場から得られた解析データに基づく、同定された新規の危険因子およびPEの管理は、臨床医にとって貴重なものである。
—————————————————————————————————————————-
★ 第81回日本血液学会学術集会 (2019/10/11-13) ★
★ OS3-10B-1
The ELTS score clearly anticipates death due to CML and molecular response rates in CML-CP
○Eriko Sato, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Michihide Tokuhira, Tomoiku Takaku, Maho Ishikawa, Tomonori Nakazato, Keiji Sugimoto, Hiroyuki Fujita, Yuta Kimura, Isao Fujioka, Norio Asou, Norio Komatsu, Masahiro Kizaki, Yoshihiro Hatta, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] EUTOS long-term survival (ELTS) score is a prognostic factor that predicts disease-specific death in patients with CML in chronic phase (CP) with imatinib-based treatment. However, it is unclear whether ELTS score is predictive of CML-related events or treatment response. This study aims to evaluate the predictability of ELTS score for prognoses and treat- ment responses patients with CML-CP.
[Patients and Methods] Clinical data were obtained retrospectively from patients enrolled in the CML Cooperative Study Group. This study included patients who were diagnosed with CML- CP between April 2001 and January 2016 and treated with any TKI as first- line therapy.
[Results] Out of 342 eligible patients, ELTS score low, intermedi- ate and high-risk were 74%, 21% and 5%, respectively. ELTS score high patients exhibited significantly worse outcomes not only in CML-related death, but also in event-free survival, progression-free survival and overall survival. Though Sokal, Hasford and EUTOS scores could predicted some survival rates, risk stratification by the ELTS score appeared to be the most predictive of patient prognoses. EUTOS and ELTS scores, but not others, could predict the achievement of MMR by 12 months. Most importantly, the ELTS score was the only scoring system that predicted the achievement of deep molecular response at any time (65.0%, 43.7%, and 23.5%, in low, in- termediate, and high risks).
[Conclusion] Compare to other risk scores, ELTS score was the most powerful risk classification tool for all four end points and molecular responses in patients with CML-CP.
[背景] EUTOS長期生存(ELTS)スコアは、イマチニブをベースとした治療を受けた慢性期(CP)のCML患者において、疾患特異的死亡を予測する予後因子である。しかし、ELTSスコアがCML関連イベントや治療効果を予測するかどうかは不明である。本研究の目的は、CML-CP患者の予後と治療効果に対するELTSスコアの予測可能性を評価することである。
[患者と方法] CML Cooperative Study Groupに登録された患者から後方視的に臨床データを入手した。本研究では、2001年4月から2016年1月までにCML-CPと診断され、第1選択療法としていずれかのTKIによる治療を受けた患者を対象とした。
[結果] 対象患者342例中、ELTSスコア低値は74%、中間リスクは21%、高リスクは5%であった。ELTSスコア高値の患者は、CML関連死のみならず、無イベント生存期間、無増悪生存期間、全生存期間においても有意に悪い転帰を示した。Sokal、Hasford、EUTOSスコアはある程度の生存率を予測できたが、ELTSスコアによるリスク層別化は患者の予後を最も予測するようであった。EUTOSスコアとELTSスコアは、12ヵ月後までのMMR達成を予測できたが、他のスコアは予測できなかった。最も重要なことは、ELTSスコアがどの時点においても深部分子学的反応の達成を予測できた唯一のスコアリングシステムであったことである(低リスク、中期リスク、高リスクにおいて、それぞれ65.0%、43.7%、23.5%)。
[結論] 他のリスクスコアと比較して、ELTSスコアはCML-CP患者における4つのエンドポイントおよび分子生物学的奏効すべてにおいて最も強力なリスク分類ツールであった。
★ OS3-10B-6
Outcome in adolescents and young adults with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with TKI
○Yuriko Fujita, Tomonori Nakazato, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Michihide Tokuhira, Maho Ishikawa, Eriko Sato, Tomoiku Takaku, Keiji Sugimoto, Hiroyuki Fujita, Isao Fujioka, Yuta Kimura, Norio Komatsu, Norio Asou, Masahiro Kizaki, Yoshihiro Hatta, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] There is little information about the clinical characteristics and outcomes in adolescents and young adults (AYA) with CML. We performed a retrospective study to evaluate the outcome in AYA with CML treated with TKI as first line therapy.
[Patients and Methods] We analyzed data from 360 patients with CML in chronic phase (CML-CP) who were extracted from the CML Cooperative Study Group database. AYA patients were defined as 18- 29 years of age at the beginning of TKI treatment.
[Results] The median follow-up time was 64 months. The median age was 53 years (range 18-89 years). One-hundred and eighty-nine patients were treated with imatinib, 98 with dasatinib and 80 with nilotinib. Forty-two patients were in the AYA group (18-29 years) and 318 patients were in the older group (30 years or over). Although AYA patients presented with more aggressive features (larger spleen size, higher WBC count, higher Sokal and Hasford score), the prob- abilities of achieving MMR and DMR were not significantly different between the AYA and the older group. The differences in the event free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) between the two groups were not statistically sig- nificant (5-year EFS: 89.6% vs. 89.8%, p=0.834, 5-year OS: 92.5% vs. 92.8%, p=0.922, respectively). Subgroup analysis of 178 patients treated with 2nd generation TKI demonstrated that the differences in the EFS and OS between the two groups were not statistically significant.
[Conclusion] Even in the 2nd generation TKI era, there were no significant differences in EFS and OS between the AYA and the older group.
[背景] 青年・若年成人CML患者の臨床的特徴や転帰に関する情報はほとんどない。我々は、1次治療としてTKIを用いたCML治療を受けたAYA患者の転帰を評価するために後方視的研究を行った。
[患者と方法] CML Cooperative Study Groupのデータベースから抽出した慢性期のCML患者360例のデータを解析した。AYA患者はTKI治療開始時の年齢が18~29歳と定義した。
[結果] 追跡期間中央値は64ヵ月であった。年齢中央値は53歳(範囲18~89歳)であった。189例がイマチニブ、98例がダサチニブ、80例がニロチニブで治療された。AYA群(18〜29歳)は42人、高齢群(30歳以上)は318人であった。AYA群はより侵攻的な特徴(脾臓サイズが大きい、WBC数が多い、SokalおよびHasfordスコアが高い)を示したが、MMRおよびDMRの達成率はAYA群と高齢群で有意差はなかった。両群間の無発症生存期間(EFS)と全生存期間(OS)に統計学的有意差は認めなかった(5年EFS:89.6%対89.8%、p=0.834、5年OS:92.5%対92.8%: 5年EFS:89.6%対89.8%、5年OS:92.5%対92.8%、p=0.922)。第2世代TKI治療を受けた178例のサブグループ解析では、両群間におけるEFSとOSは統計学的に有意差は認めなかった。
[結論] 第2世代TKI時代においても、AYA群と高齢者群との間でEFSとOSに有意差は認めなかった。
★ OS3-11B-5
Smoking influences the outcomes of patients receiving TKIs for CML in the chronic phase
○Noriyoshi Iriyama, Michihide Tokuhira, Eriko Sato, Keiji Sugimoto, Tomoiku Takaku, Maho Ishikawa, Tomonori Nakazato, Hiroyuki Fujita, Yuta Kimura, Isao Fujioka, Norio Asou, Norio Komatsu,
Masahiro Kizaki, Yoshihiro Hatta, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
In this study, we investigated the clinical characteristics, treatment out- comes, and complications related to patients undergoing tyrosine kinase in- hibitor (TKI) treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in the chronic phase as a function of their prior or current smoking status. We extracted data from the CML Cooperative Study Group database; smokers were defined as patients who previously smoked or were current smokers. There were no significant demographic differences between smokers and non- smokers other than a male predominance and higher hemoglobin levels in the former. Risk stratification according to the Sokal, Hasford, European Treatment and Outcome Study (EUTOS), and EUTOS long-term survival scores showed equal distribution between smokers and non-smokers. The event-free and transformation-free survival rates were significantly lower in smokers than in non-smokers; however, the overall survival and cumulative CML-related death rates did not differ between the groups. Response to TKI therapy, including major molecular response rates by 6, 12, and 18 months, deep molecular response rates by 24 and 36 months, and depth of best response were similar between groups. The major causes of death in patients who died were not related to CML but rather to vascular adverse events, which were observed with markedly higher frequencies among smokers. The incidences of second malignancies were similar in both groups. Our findings highlight the detrimental influence of tobacco exposure on the clini- cal outcomes of patients with CML who are undergoing TKI treatment.
本研究では、慢性期の慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)に対するチロシンキナーゼインヒビター(TKI)治療を受けている患者の臨床的特徴、治療成績、および合併症について、喫煙歴または現在の喫煙状況別に検討した。CML Cooperative Study Groupのデータベースからデータを抽出した。喫煙者は、過去に喫煙していた患者または現在喫煙している患者とした。喫煙者と非喫煙者の間には、男性優位と前者でヘモグロビン値が高いこと以外に、人口統計学的な有意差はみられなかった。Sokal、Hasford、European Treatment and Outcome Study(EUTOS)、EUTOS長期生存スコアによるリスク層別化では、喫煙者と非喫煙者の分布は同等であった。無イベント生存率および無転移生存率は、喫煙者が非喫煙者より有意に低かったが、全生存率および累積CML関連死亡率に群間差はなかった。6ヵ月、12ヵ月、18ヵ月までの主要分子奏効率、24ヵ月、36ヵ月までの深部分子奏効率、最良反応の深さなどのTKI療法に対する奏効率は群間で同様であった。死亡した患者の主な死因はCMLではなく、むしろ血管系の有害事象であり、喫煙者に顕著に高い頻度で観察された。二次悪性腫瘍の発生率は両群で同程度であった。我々の知見は、TKI治療を受けているCML患者の臨床転帰にタバコ曝露が有害な影響を及ぼすことを強調するものである。
—————————————————————————————————————————–
★ 第80回日本血液学会学術集会 (2018/10/12-14) ★
★ OS2-9B-3
Analysis of cardiovascular risk factors in nilotinib-treated Japanese CML patients
○Isao Fujioka, Tomoiku Takaku, Michihide Tokuhira, Yuta Kimura, Eisaku Iwanaga, Keiji Sugimoto, Tomonori Nakazato, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Eriko Sato, Maho Ishikawa, Hiroyuki Fujita, Norio Asou, Yoshihiro Hatta, Masahiro Kizaki, Norio Komatsu, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
Treatment strategy for CML has changed significantly since the emergence of the first-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) imatinib, and treatment based on TKIs have dramatically improved the outcome in the majority of chronic phase(CP)-CML patients. Nowadays, second generation TKIs brought about faster, deeper clinical responses. From 2011, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) were revealed as unignor- ably severe adverse events (AEs) during TKI therapy. Thereafter, incidences of CVDs increasing with dose escalation and treatment duration were also reported in a long-term follow-up of the clinical trial for nilotinib. However, there is no available data about the risk factors of CVDs among nilotinib-treated Japanese CML patients. Here we analyzed the risk factors in nilotinib-treated patients selected from a cohort of 369 Japanese CML patients enrolled in a retrospective observational study of the CML Cooperative Study Group. Among the 138 nilotinib-treated patients analyzed, 12 (8.7%) CVD events including 7 ischemic heart disease, 3 cerebral infarction, and 2 peripheral arterial occlusive disease were reported during the study period. The results of multivariate analysis indicated 4 factors (age, dyslipidemia, hyperten- sion, diabetes) with more than 1.00 hazard ratio (HR) were extracted. Four factors were extracted as the possible influencing factors of CVDs in nilotinib-treated pa- tients and development of a risk assessment tool more weight on these factors is needed for the prediction of CVDs in nilotinib-treated Japanese patients.
[背景】慢性期の慢性骨髄性白血病(ND-CML-CP)と新たに診断された患者において、チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(TKI)の優れた有効性が証明されているが、年齢の影響は十分に理解されていない。
[患者および結果]ファーストラインとしてダサチニブ(Das)を投与された65歳未満の患者61人(非高齢群、NE-G)と65歳以上の患者37人(高齢群、E-G)の解析を行った。2群間の患者背景では、E-G群で高年齢、観察期間短縮、Sokalスコア高値、ELTSスコア高値が有意差をもって認められた。最終観察時の状態については、NE-G群では53.9%、E-G群では40.5%がファーストラインとしてDasを継続していた。同時に、様々な理由でTKIを中止した割合は、NE-Gで11.5%、E-Gで24.3%であったが、Das後のセカンドライン、サードラインの割合はほぼ同率であった。有効性に関しては、NE-GとE-GのDas治療中の累積MMR率は、開始後6カ月でそれぞれ37.7%と18.9%であった。12ヵ月後,24ヵ月後の累積MMR率はそれぞれ63.9%,37.8%,78.7%,51.4%であった。各時点で有意差は認められなかった。転帰に関しては、NE-Gでは2例、E-Gでは6例が死亡した。5年OSはNE-Gで88.8%、E-Gで84.6%であった。
[結論]この後方視研究では、ND-CML-CP患者において、Das投与が年齢を問わず同様の有効性を示した。
★ OS2-9B-4
Additional chromosomal abnormalities at diagnosis and their impact on treatment response in CML
○Maho Ishikawa, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Michihide Tokuhira, Tomoiku Takaku, Eriko Sato, Keiji Sugimoto, Tomonori Nakazato, Eisaku Iwanaga, Hiroyuki Fujita, Yuta Kimura, Isao Fujioka, Norio Komatsu, Norio Asou, Masahiro Kizaki, Yoshihiro Hatta, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have improved the prognosis of pa- tients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). In the imatinib era, major route addi- tional chromosomal abnormalities (ACAs) at diagnosis affected shorter survival and risk of disease progression. However, it remains unclear whether major route ACA is still a poor prognostic marker in the second-generation (2G) TKI era.
[Patients and Methods] We analyzed the data of patients (pts) with CML in the chronic phase (CP) who were extracted from the CML Cooperative Study Group database in a retrospective fashion.
[Results] Out of 330 eligible pts, 296 (89.7%) had sole t(9;22)(q34;q11) and 34 (10.3%) had ACA, including 9 major route and 25 minor route ACAs. The major route ACAs included der(22)t(9;22) in 7 pts, +8 in 1, and +19 in 1. Out of 9 pts with major route ACA, 5 were treated with imatinib, 3 with nilotinib, and 1 with dasatinib as first-line therapy. None experienced disease progression among pts with major route ACA. In particular, all of 4 treated with 2G-TKI showed excellent response; 4 attained MMR and 3 MR4.5 by 12 months. The log-rank test revealed that pts with major route ACA did not show inferior survival compared to those without this abnormality.
[Conclusion] Our retrospective study revealed a favorable response to 2G-TKI in pts with major route ACA. Therefore, our data suggest that the introduction of 2G-TKIs might be recommended for the treatment of CML-CP with major route ACA.
[背景] チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(TKI)は慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)患者の予後を改善してきた。イマチニブ時代には、診断時の主要ルート付加型染色体異常(ACA)が生存期間の短縮と病勢進行のリスクに影響を及ぼしていた。しかし、主要経路ACAが第2世代(2G)TKI時代においても予後不良マーカーであるかどうかは不明である。
[患者と方法]CML Cooperative Study Groupのデータベースから抽出した慢性期のCML患者のデータをレトロスペクティブに解析した。
[結果]適格患者330人のうち、296人(89.7%)が単独でt(9;22)(q34;q11)を有し、34人(10.3%)がACAを有していた。主要経路ACAにはder(22)t(9;22)が7例、+8が1例、+19が1例含まれていた。主要経路ACAを認めた9例のうち、5例はイマチニブ、3例はニロチニブ、1例はダサチニブで初回治療を受けた。主要ルートACA患者のうち、病勢進行した患者はいなかった。特に、2G-TKIで治療された4人全員が優れた奏効を示し、12ヵ月までに4人がMMRを、3人がMR4.5を達成した。log-rank検定の結果、major route ACAを有する症例は、この異常のない症例と比較して生存率が劣ることはなかった。
[結論]我々の後方視的研究により、major route ACAを有する症例において2G-TKIが良好に奏効することが明らかになった。したがって、我々のデータは、主要ルートACAを有するCML-CPの治療に2G-TKIの導入が推奨される可能性を示唆している。
★ PS2-7-3
An updated analysis of vascular adverse events in large cohort of TKI treated Japanese CML patients
○Tomoiku Takaku, Isao Fujioka, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Michihide Tokuhira, Yuta Kimura, Eisaku Iwanaga, Eriko Sato, Maho Ishikawa, Tomonori Nakazato, Keiji Sugimoto, Hiroyuki Fujita, Norio Asou, Masahiro Kizaki, Yoshihiro Hatta, Norio Komatsu, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
Treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) has dramatically changed since the emergence of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) imatinib. However, longer treatment duration gave rise to various kinds of unexpected adverse events (AEs). Especially, vascular AEs (VAEs) are considered a more fatal complication of TKI treatment. Here we report about an updated investigation of the vascular safety issue among Japanese CML patients who were enrolled in the CML Cooperative Study Group (CML-CSG). A surveillance data of 369 patients was conducted in this analysis. Briefly, the study included patients who were diagnosed with CML from April 2001 to January 2016, whose median age was 53 years old and median time of follow up was 62.8 months. Patients in the blastic phase were excluded. All patients who de- veloped VAEs were estimated the 1000 person-years risk of developing VAEs. Twenty-five VAE events in 23 (6.2%) patients were reported during the study period. At the incidence of VAE, 8, 12, 4, and 1 events who had been treated with imatinib, nilotinib, dasatinib, and bosutinib, respectively. The VAEs included 13 ischemic heart disease (IHD), 8 cerebral infarction, and 4 peripheral artery occlusive disease cases. The incidence rates of IHD during nilotinib therapy were higher than those during imatinib, dasatinib, and bosutinib therapy.In conclusion, incidence of IHD re- quires closer monitoring for nilotinib-treated patients. More detailed investigations and long-term analysis of therapy-related VAE cases are needed for improving safe- ty during TKI therapy.
慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)の治療は、チロシンキナーゼ阻害剤(TKI)であるイマチニブの登場以来、劇的に変化した。しかし、治療期間が長くなるにつれて、予期せぬさまざまな有害事象(AE)が生じるようになった。特に血管系有害事象(VAE)は、TKI治療のより致命的な合併症と考えられている。我々は、CML協同研究グループ(CML-CSG)に登録された日本人CML患者を対象としたVAEに関する最新の調査について報告する。本解析では、369例のサーベイランスデータを用いた。2001年4月から2016年1月までにCMLと診断された患者を対象とし、年齢中央値は53歳、追跡期間中央値は62.8ヵ月であった。芽球期患者は除外した。VAEを発症した全患者について、VAE発症の1000人年リスクを推定した。研究期間中、23例(6.2%)において25件のVAEが報告された。VAEの発生率は、イマチニブ、ニロチニブ、ダサチニブ、ボスチニブによる治療を受けた患者で、それぞれ8、12、4、1イベントであった。VAEの内訳は、虚血性心疾患(IHD)13例、脳梗塞8例、末梢動脈閉塞性疾患4例であった。結論として、ニロチニブ治療中のIHD発症率は、イマチニブ、ダサチニブ、ボスチニブ治療中よりも高かった。TKI治療中の安全性を向上させるためには、治療関連VAE症例のより詳細な調査と長期的な解析が必要である。
—————————————————————————————————————————-
★ 第79回日本血液学会学術集会 (2017/10/22-24) ★
★ OS3-14A-2
Incidence of second malignancies of chronic myeloid leukemia during TKI treatment
○Tomonori Nakazato, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Michihide Tokuhira, Maho Ishikawa, Eriko Sato, Tomoiku Takaku, Kei-Ji Sugimoto, Hiroyuki Fujita, Isao Fujioka, Norio Komatsu, Norio Asou, Masahiro Kizaki, Yoshihiro Hatta, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
Background We performed a retrospective study to evaluate the incidence of sec- ond malignancies (SM) in CML patients treated with TKI. Patients and Methods: We analyzed data from 339 patients with CML who were extracted from the CML Coop- erative Study Group database. Standardized incidence ratio (SIR) was calculated to assess the risk of SM using data from the Cancer Registries in Japan.
Results:Follow-up was 1931 person-years (median 5.4 years; range,0.6-15.0). SM developed in 14 patients (4.1%, 10 male, 4 female) after the start of TKI. The median age was 69 years (range 36-86) at the time of CML diagnosis and 72.5 years (range 45-90) at the time of SM diagnosis. Ten patients were treated with imatinib, 3 pa- tients with dasatinib and 1 patient with nilotinib as the initial treatment. The median duration from the start of TKI to the diagnosis of SM was 3.3 years (range 0.1-10.5). The SMs included stomach(3), colon(2), esophagus(1), tongue(1), breast(1), prostate(1), lung(1), liver(1), ovary(1), larynx(1), and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (1). The SIR for all malignancies was 1.05 (95%CI 0.50-1.93) for men and 1.08 (95%CI 0.29-2.76) for women. The difference in the overall survival of patients with or without SM was not statistically significant. Subgroup analysis of 162 patients treated with 2nd generation TKI (92 dasatinib, 70 nilotinib) demonstrated that the SIR for all malignancies was 1.36 (95%CI 0.37-3.48) for men and 0 for women.
Conclusion: Even in the 2nd generation TKI era, the incidence of SM in CML patients during TKI was the same as that in the general population.
[背景]我々は、TKI治療を受けたCML患者における二次悪性腫瘍(SM)の発生率を評価するためにレトロスペクティブ研究を行った。患者と方法 CML Coop- erative Study Groupのデータベースから抽出したCML患者339例のデータを解析した。標準化罹患率比(SIR)は、日本のがん登録のデータを用いてSMのリスクを評価するために算出した。
[結果]追跡期間は1931人年(中央値5.4年、範囲0.6-15.0)であった。SMはTKI開始後14例(4.1%、男性10例、女性4例)に発症した。年齢中央値はCML診断時69歳(範囲36-86)、SM診断時72.5歳(範囲45-90)であった。初回治療としてイマチニブが10例、ダサチニブが3例、ニロチニブが1例であった。TKI開始からSM診断までの期間中央値は3.3年(範囲0.1〜10.5)であった。SMの内訳は、胃(3)、結腸(2)、食道(1)、舌(1)、乳房(1)、前立腺(1)、肺(1)、肝臓(1)、卵巣(1)、喉頭(1)、非ホジキンリンパ腫(1)であった。全悪性腫瘍のSIRは、男性で1.05(95%CI 0.50-1.93)、女性で1.08(95%CI 0.29-2.76)であった。SMの有無による全生存期間の差は統計学的に有意ではなかった。第2世代TKI治療を受けた162例(ダサチニブ92例、ニロチニブ70例)のサブグループ解析では、全悪性腫瘍のSIRは男性で1.36(95%CI 0.37-3.48)、女性で0であった。
[結論] 第2世代TKI時代においても、TKI施行中のCML患者におけるSMの発生率は一般集団と同じであった。
★ OS3-14A-3
Analysis of vascular adverse events in TKI treated large cohort Japanese CML patients
○Isao Fujioka, Tomoiku Takaku, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Michihide Tokuhira, Eriko Sato, Maho Ishikawa, Tomonori Nakazato, Kei-Ji Sugimoto, Hiroyuki Fujita, Norio Asou, Masahiro Kizak, Yoshihiro Hatta, Norio Komatsu, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
Treatment of chronic phase (CP) Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) has dramatically changed since the emergence of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) imatinib. How- ever longer treatment duration gave rise to various kinds of unexpected adverse events (AEs). Especially, vascular AEs (VAEs) are considered a more fatal compli- cation of TKI treatment. We investigated the vascular safety issue among 320 Japa- nese patients who were enrolled in the CML Cooperative Study Group. A surveil- lance data of 320 patients enrolled in the CML Cooperative Study Group was conducted in this analysis. Briefly, the study included patients who were diagnosed with CML-CP from April 2001 to January 2016, whose median age was 57 years old (15-80) and median time of follow up was 64.2 months. Patients in the accelerated or blastic phase (AP/BP) were excluded. All patients who developed VAEs were estimated the 1000 person-years risk of developing VAEs and the patients’ 10-year risk during TKI treatment using 3 risk assessment tools. 16 (5.0%) cases of VAEs were reported during the study period. 7, 3 and 1 cases were treated by imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib, respectively. 4 cases were a switch from imatinib to nilotinib, and 1 case was a switch from dasatinib to nilotinib. The VAEs were 9 ischemic heart dis- ease (IHD), 5 cerebral infarction (CI), and 2 peripheral artery occlusive disease (PAOD) cases. The incidence rate of all kinds of VAEs per 1000 person-years were higher in the nilotinib-treated CML patients, even though the incidence were lower in Japanese as compared to the European cohort.
慢性期(CP)慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)の治療は、チロシンキナーゼ阻害剤(TKI)イマチニブの出現以来劇的に変化した。しかし、治療期間が長くなるにつれ、予期せぬさまざまな有害事象(AE)が生じるようになった。特に血管系の有害事象(VAE)は、TKI治療の致命的な問題であると考えられている。我々は、CML Cooperative Study Groupに登録された320人の日本人患者を対象に、血管安全性の問題を調査した。本解析では、CML Cooperative Study Groupに登録された320例のサーベイランスデータを用いた。2001年4月から2016年1月までにCML-CPと診断された患者を対象とし、年齢中央値は57歳(15~80歳)、追跡期間中央値は64.2ヵ月であった。加速期または芽球期(AP/BP)の患者は除外された。VAEを発症した全患者は、3つのリスク評価ツールを用いて、VAE発症の1000人年リスクとTKI治療中の患者の10年リスクを評価した。試験期間中に16例(5.0%)のVAEが報告された。イマチニブ、ニロチニブ、ダサチニブによる治療がそれぞれ7例、3例、1例であった。4例はイマチニブからニロチニブへの切り替え、1例はダサチニブからニロチニブへの切り替えであった。VAEは虚血性心疾患(IHD)9例、脳梗塞(CI)5例、末梢動脈閉塞性疾患(PAOD)2例であった。ニロチニブ治療を受けたCML患者では、1,000人年当たりのすべての種類のVAEの発生率が高かった。
★ OS3-14A-4
Efficacy and safety of the reduced dasatinib therapy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia
○Yuta Kimura, Tomoiku Takaku, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Eriko Sato, Tomonori Nakazato, Kei-Ji Sugimoto, Hiroyuki Fujita, Maho Ishikawa, Isao Fujioka, Michihide Tokuhira, Norio Asou, Yoshihiro Hatta, Norio Komatsu, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] The second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as dasatinib (Das) has potent efficacy against chronic myeloid leukemia in the chronic phase (CML-CP).However, it is unclear whether dose modification for the management of adverse events (AEs) inversely affects clinical outcomes. In this retrospective study, we aimed to explore the effects of modified dose of Das on CMP-CP in a real-world setting.
[Patients and Methods] Among 339 patients(pts) with CML in the CML- Cooperate Study Group database, 92 received Das as an initial therapy. We as- sessed the efficacy and safety of Das, and compared the outcomes of pts receiving a dose of 100 mg/day (standard dose group: St-g) with those of pts receiving less than 100 mg/day (low dose group: Lo-g).
[Results] Median age was 58 years. Dura- tion of median observation snd Das administration were 906.5 and 638 days, re- spectively. The ratio of pts who achieved MMR and MR4.5 at any time under Das treatment was 82.3% and 45.6%, respectively. Continuation rate of Das treatment was 60.5%.There were 59 and 33 pts classified into St-g and Lo-g, respectively. Me- dian age was significantly higher in Lo-g compared to St-g (65 vs. 56 years, p = 0.00241). In terms of efficacy, MMR/MR4.5 ratios at any time, and at 1 year, were not significantly different between 2 groups. The discontinuation rates were 13.6% in St-g and 6% in Lo-g, mainly due to plural effusion.
[Conclusion] In this retrospective study, similar efficacy and better safety were observed in pts receiving the reduced of Das.
[背景] ダサチニブ(Das)に代表される第二世代チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬は、慢性期の慢性骨髄性白血病(CML-CP)に対して強力な有効性を有する。しかし、有害事象(AE)管理のための用量変更が臨床転帰に悪影響を及ぼすかどうかは不明である。本後方視的解析では、実臨床におけるDasの用量変更がCMP-CPに及ぼす影響を検討することを目的とした。
[患者と方法] CML- Cooperate Study Groupデータベースに登録されたCML患者339例のうち、92例にDasが初回治療として投与された。Dasの有効性と安全性を検討し、100mg/日投与群(標準用量群:St-g)と100mg/日未満投与群(低用量群:Lo-g)の治療成績を比較した。
[結果] 年齢中央値は58歳であった。観察期間およびDas投与期間の中央値は、それぞれ906.5日および638日であった。Das投与中にMMRとMR4.5を達成した患者の割合はそれぞれ82.3%と45.6%であった。Das治療の継続率は60.5%であった。St-gとLo-gに分類された患者はそれぞれ59人と33人であった。患者の年齢はSt-g群に比べLo-g群で有意に高かった(65歳 vs 56歳、p = 0.00241)。有効性に関しては、MMR/MR4.5比はいずれの時点においても、また1年後においても両群間に有意差はなかった。中止率はSt-g群で13.6%、Lo-g群で6%であり、その主な原因は複数の胸水であった。
[結論] この後方視的研究では、Dasを減量した群では同様の有効性とより良好な安全性が観察された。
★ PS2-8-4
Analysis of contributing factors to lymphocytosis during dasatinib therapy for CML
○Kei-Ji Sugimoto, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Isao Fujioka, Tomoiku Takaku, Eriko Sato, Maho Ishikawa, Tomonori Nakazato, Hiroyuki Fujita, Masahiro Kizaki, Norio Komatsu, Norio Asou, Yoshihiro Hatta, Michihide Tokuhira, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
Background: Factors that influence the incidence of lymphocytosis and the treatment response among Japanese patients receiving dasatinib remain elusive.
Patient and Methods: This retrospective study included 139 patients (male, n = 89; female, n = 50) who had been treated with dasatinib, from a database of patients constructed by the Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) Cooperative Study Group in Japan. Among these patients, 48 (34.5%) had lymphocytosis defined as a lymphocyte count ≥ 3.6 x 109/L on at least two occasions after 28 days of treatment, and 86 (61.9%) did not. We assessed factors such as age, sex, CMV-IgG serology, initial dose of dasatinib, and treatment regimen that might affect the incidence of lymphocytosis. The total cumulative incidence of lymphocytosis was determined, and fac- tors were identified in multivariate analyses using the Cox proportional hazards re- gression model. Associations between lymphocytosis and therapeutic effects within one year of starting first-line therapy with dasatinib were examined using Fisher’s exact test. Results: Multivariate analysis of data from 41 patients without missing values revealed a high incidence of lymphocytosis among males (hazard ratio [HR], 0.1768; p = 0.006). During the first 12 months of dasatinib therapy in the first-line setting, the incidence of lymphocytosis was closely associated with the achievement of a major molecular response (p = 0.0107). Conclusion: Male sex is an important factor that is associated with the incidence of lymphocytosis, which is closely in- volved in the therapeutic response to dasatinib.
[背景] ダサチニブを投与された日本人患者におけるリンパ球減少症の発症率および治療効果に影響を及ぼす因子は、依然として不明である
[患者と方法] 本レトロスペクティブ研究は、日本の慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)協同研究グループによって構築された患者データベースから、ダサチニブによる治療を受けた139例(男性、n=89;女性、n=50)を対象とした。これらの患者のうち、48例(34.5%)は治療開始28日後に少なくとも2回、リンパ球数≧3.6×109/Lと定義されるリンパ球増加を認め、86例(61.9%)は認めなかった。年齢、性別、CMV-IgG血清学的検査、ダサチニブの初回投与量、治療レジメンなど、リンパ球症の発生率に影響を及ぼす可能性のある因子を評価した。リンパ球症の全累積発生率を求め、Cox比例ハザード回帰モデルを用いた多変量解析で因子を同定した。ダサチニブによる一次治療開始後1年以内のリンパ球症と治療効果との関連をフィッシャーの正確検定を用いて検討した。
[結果] 欠測のない41例のデータを多変量解析したところ、リンパ球減少は男性に多くみられた(ハザード比[HR]、0.1768;p = 0.006)。一次治療におけるダサチニブ治療の最初の12ヵ月間、リンパ球減少症の発生率は主要分子応答の達成と密接に関連していた(p = 0.0107)。
[結論] 男性の性別はリンパ球症の発生率と関連する重要な因子であり、ダサチニブに対する治療効果に密接に関与している。
★ PS2-9-3
The introduction of 2nd TKIs may reduce the prognostic impact of EUTOS high-risk patients
○Eriko Sato, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Michihide Tokuhira, Tomoiku Takaku, Maho Ishikawa, Tomonori Nakazato, Kei-Ji Sugimoto, Hiroyuki Fujita, Isao Fujioka, Norio Asou, Norio Komatsu, Masahiro Kizak, Yoshihiro Hatta, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] The European Treatment and Outcome Study (EUTOS) score predicts treatment response and progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in chronic phase (CP) treated with imatinib-based regimen. Our study aims to verify whether the introduction of second generation TKIs (2nd TKIs) affects the predictive ability of EUTOS score of patients with CML-CP.
[Patients and Methods] Clinical data were ob- tained retrospectively from patients enrolled in the CML Cooperative Study Group. Patients with CML-CP treated with any TKI as first line therapy were enrolled to the study, and were classified by the diagnosed date before March 2009 as imatinib group (IM), and after April 2009 as the 2nd TKI group (2G).
[Results] Out of 328 patients, 107 (34%) were assigned to IM and 221 (66%) were assigned to 2G. 265 patients were classified as EU- TOS low-risk, of which 83 were in IM and 182 were in 2G. 46 patients were considered high-risk, of which 19 were in IM and 27 were in 2G. EUTOS high-risk patients score exhibited significantly worse outcomes in event-free survival, PFS, and CML-associated death compared to those considered low-risk. Importantly, the EUTOS high-risk patients showed worse clinical outcomes than those with low-risk in IM; however, prognostic effect was less in 2G.
[Conclusion] EUTOS score was predictive of risk-associated clinical outcomes in IM; however, failed to predict the 2nd TKI group. The 2nd TKIs may improve treatment outcomes in high-risk patients with CML-CP.
[背景] EUTOS(European Treatment and Outcome Study)スコアは、イマチニブをベースとしたレジメンで治療された慢性期の慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)患者における治療効果と無増悪生存期間(PFS)を予測する。本研究の目的は、第二世代TKI(2nd TKI)の導入がCML-CP患者のEUTOSスコアの予測能力に影響を及ぼすかどうかを検証することである。
[患者と方法] CML Cooperative Study Groupに登録された患者からレトロスペクティブに臨床データを収集した。2009年3月以前の診断日をイマチニブ群(IM)、2009年4月以降を2nd TKI群(2G)とした。
[結果] 328例中、107例(34%)がIM群、221例(66%)が2G群に割り付けられた。265例がEU-TOS低リスクに分類され、うち83例がIM群、182例が2G群であった。46例が高リスクとされ、うち19例がIM、27例が2Gであった。EUTOS高リスク患者は、低リスク患者と比較して、無イベント生存期間、PFS、CML関連死において有意に悪い転帰を示した。重要なことは、EUTOS高リスク患者はIMでは低リスク患者より悪い臨床転帰を示したが、2Gでは予後への影響は少なかったことである。
[結論] EUTOS スコアは、IM のリスク関連臨床転帰を予測したが、2nd TKI 群を予測することはできなかった。2ndTKIはCML-CPの高リスク患者の治療成績を改善する可能性がある。
★ PS2-9-4
Efficacy and safety of the reduced nilotinib therapy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia
○Michihide Tokuhira, Kei-Ji Sugimoto, Tomonori Nakazato, Maho Ishikawa, Isao Fujioka, Tomoiku Takaku, Noriyoshi Iriyama, Eriko Sato, Hiroyuki Fujita, Norio Asou, Yoshihiro Hatta, Norio Komatsu, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background] In the clinical setting, dose modification of tyrosine kinase inhibitors is important to achieve proper therapy in terms of efficacy and safety. However, clinical effects of modified dose of nilotinib (Nilo) for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in the chronic phase (CP) have rarely been reported.
[Patients and Methods] We ana- lyzed data of 339 patients (pts) with CML from the CML Cooperative Study Group database. Seventy patients received Nilo as an initial therapy, and 67 pts continued the therapy over a year. To investigate the potency of the modified Nilo dose, we compared the efficacy and safety between the pts receiving 600 mg/day Nilo dose (Standard group: St-g) and ptsreceiving less than 450 mg/day or less dose (Re- duced group: Re-g).
[Results] The number of pts in the St-g and Re-g were 50 and 17, respectively. The median age was significantly higher in Re-g (51.7 y.o. and 61.4 y.o., respectively). Median duration of Nilo administration, and the ratio of MMR at any time were not significant difference between 2 groups. The ratio of MMR at a year was not significant difference as well. Focusing on MR 4.5, there was no signifi- cant difference between the groups regarding the ratio by any time or by a year and the Nilo duration. Although 2 pts died, the reasons were not related to CML. Regard- ing AE, cardiovascular events developed in 3 pts; one in the St-g and two in the Re- g.
[Conclusion]This retrospective study demonstrated similar efficacy and safety of reduced-dose Nilo therapy (450 mg/day or less) and the standard therapy (600 mg/day) for CML-CP.
[背景]臨床において、チロシンキナーゼ阻害剤の用量変更は、有効性と安全性の観点から適切な治療を行うために重要である。しかし、慢性期(CP)の慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)に対するニロチニブ(Nilo)の用量変更の臨床効果はほとんど報告されていない。
[患者と方法] 70人の患者が初回治療としてNilo投与を受け、67人の患者が1年間治療を継続した。Nilo用量調節の有効性を検討するため、Nilo600mg/日投与群(標準群:St-g)と450mg/日以下投与群(減量群:Re-g)の有効性と安全性を比較した。年齢中央値はRe-g群で有意に高かった(それぞれ51.7歳、61.4歳)。Nilo投与期間の中央値、および累積MMR比は両群間に有意差はなかった。1年後のMMR率も有意差はなかった。MR4.5に着目すると、MR4.5とNilo投与期間との間に有意差はなかった。2例が死亡したが、死亡理由はCMLとは無関係であった。
[結論】この後方視的研究では、CML-CPに対するNilo減量療法(450mg/日以下)と標準療法(600mg/日)の有効性と安全性が同等であることが示された。
—————————————————————————————————————————–
★ 22nd Congress of European Hematology Association (EHA) (2017/06/22-25) ★
★ E1058
ANALYSIS OF VASCULAR ADVERSE EVENTS IN TKI TREATED JAPANESE CML PATIENTS: RETROSPECTIVE LARGE COHORT STUDY OF CML COOPERATIVE STUDY GROUP
○I. Fujioka, T. Takaku, N. Iriyama, M. Tokuhira, E. Sato, M. Ishikawa, T. Nakazato, K.-J. Sugimoto, H. Fujita, N. Asou, M. Kizaki, Y. Hatta, N. Komatsu, T. Kawaguchi.
[Background] Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a disease of hematopoietic stem cells resulting from oncogenic chromosome translocation that leads to the formation of the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene.Treatment of chronic phase (CP) CML has dramatically changed since the emergence of the first-in class tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) imatinib, and treatment based on TKI has improved the outcome in the majority of CP-CML patients. Nowadays, second generation TKIs are available and brought about faster and deeper clinical responses, and lower disease progression rate than imatinib. On the other hand, longer treatment duration and the increased types of TKIs gave rise to various kinds of unexpected adverse events (AEs). In 2011, drug-induced peripheral artery occlusive disease (PAOD) was first reported, followed by vascular AEs (VAEs) including ischemic heart disease (IHD) and cerebral infarction (CI). Furthermore, it became clear that the incidence of VAEs increased with the dose and treatment duration, therefore VAEs are considered a more fatal complication of TKI treatment. However, there is no available data about the incidence of VAEs in Japanese patients.
[Aims] We investigated the vascular safety issue and estimated the 1000 person-years risk of developing VAEs during TKI treatment, including imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib, using 3 risk assessment tools among 320 Japanese patients who were enrolled in the CML Cooperative Study Group.
[Methods] A surveillance data of 320 patients enrolled in the CML Cooperative Study Group was conducted in this analysis. Briefly, the study included patients who were diagnosed with CML-CP from April 2001 to January 2016, whose median age was 57 years old (15-80) and median time of follow up was 64.2 months. Patients in the accelerated or blastic phase (AP/BP) were excluded. The study was approved by the research ethics boards of each institutions and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients who developed VAEs were analyzed using 3 risk assessment tools (SCORE chart, Framingham risk score, Suita-score) to estimate the patients’ 10-year risk of VAEs.
[Results] Among the 320 newly diagnosed CML-CP patients, 16 (5.0%) cases of VAEs were reported during the study period. Seven cases were treated by imatinib, 3 cases by nilotinib, 1 case by dasatinib, 4 cases were a switch from imatinib to nilotinib, and 1 case was a switch from dasatinib to nilotinib. The VAEs were 9 IHD, 5 CI, and 2 PAOD cases. Results from the 3 risk assessment tools are as follows: SCORE (2 low, 9 moderate, 1 high, 4 very high risk), Framingham score (3 low, 5 moderate, 7 high risk), and Suita-score (13 low, 1 intermediate, 1 high risk). The incidence rate of IHD and CI per 1000 person-years were 5.26 and 2.92 in the enrolled CML-CP patients, 4.65 and 2.33 in the imatinib-treated patients, 14.34 and 10.75 in the nilotinib-treated patients, 4.08 and no case in the dasatinib-treated patients, and 1.787 and 3.342 in the age-matched general population, respectively. Among the 320 newly diagnosed CML-CP patients, 16 (5.0%) cases of VAEs were reported during the study period. Seven cases were treated by imatinib, 3 cases by nilotinib, 1 case by dasatinib, 4 cases were a switch from imatinib to nilotinib, and 1 case was a switch from dasatinib to nilotinib. The VAEs were 9 IHD, 5 CI, and 2 PAOD cases. Results from the 3 risk assessment tools are as follows: SCORE (2 low, 9 moderate, 1 high, 4 very high risk), Framingham score (3 low, 5 moderate, 7 high risk), and Suita-score (13 low, 1 intermediate, 1 high risk). The incidence rate of IHD and CI per 1000 person-years were 5.26 and 2.92 in the enrolled CMLCP patients, 4.65 and 2.33 in the imatinib-treated patients, 14.34 and 10.75 in the nilotinib-treated patients, 4.08 and no case in the dasatinib-treated patients, and 1.787 and 3.342 in the age-matched general population, respectively.
[Summary/Conclusions]The incidence rate of IHD per 1000 person-years were higher in the nilotinib- and lower in imatinib- and dasatinib-treated CML patients, and the patients showed almost the same rate of CI as compared with the age-matched general population, even though the incidence of VAEs were lower in Japanese as compared to the European cohort. More patients were estimated to have very-high and high risk of VAEs in the SCORE and Framingham risk score assessment tools as compared with the Suita-score tool.
[背景] 慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)は、BCR-ABL1融合遺伝子の形成につながるがん原性染色体転座に起因する造血幹細胞の疾患である。ファースト・イン・クラスのチロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(TKI)であるイマチニブの登場以来、慢性期(CP)CMLの治療は劇的に変化し、TKIに基づく治療はCP-CML患者の大部分で転帰を改善した。現在では、第2世代のTKIが利用可能であり、イマチニブよりも迅速かつ深い臨床効果をもたらし、病勢進行率も低下している。その一方で、治療期間の延長とTKIの種類の増加により、予期せぬ様々な有害事象が発生しました。2011年には、薬剤による末梢動脈閉塞性疾患(PAOD)が最初に報告され、虚血性心疾患(IHD)や脳梗塞(CI)などの血管性有害事象(VAE)がそれに続いた。さらに、VAEの発生率は投与量や治療期間とともに増加することが明らかになり、VAEはTKI治療のより致命的な合併症と考えられている。しかし、日本人におけるVAE発症率に関するデータはない。
[目的】CML Cooperative Study Groupに登録された320名の日本人患者を対象に、血管安全性の問題を調査し、3つのリスク評価ツールを用いてイマチニブ、ニロチニブ、ダサチニブを含むTKI治療中にVAEを発症する1000人年のリスクを推定した。
[方法】本解析では、CML Cooperative Study Groupに登録された320例のサーベイランスデータを用いた。簡単に述べると、本研究は2001年4月から2016年1月までにCML-CPと診断された患者を対象とし、年齢中央値は57歳(15~80歳)、追跡期間中央値は64.2ヵ月であった。加速期または芽球期(AP/BP)の患者は除外された。本研究は、各施設の研究倫理委員会の承認を受け、ヘルシンキ宣言に従って実施された。VAEを発症した全患者を3つのリスク評価ツール(SCORE chart、Framingham risk score、Suita-score)を用いて分析し、患者の10年間のVAEリスクを推定した。
[結果】新たにCML-CPと診断された320例のうち、調査期間中に16例(5.0%)のVAEが報告された。イマチニブによる治療が7例、ニロチニブによる治療が3例、ダサチニブによる治療が1例、イマチニブからニロチニブへの切り替えが4例、ダサチニブからニロチニブへの切り替えが1例であった。VAEはIHDが9例、CIが5例、PAODが2例であった。3つのリスク評価ツールの結果は以下の通りである: SCORE(低リスク2例、中等度9例、高リスク1例、超高リスク4例)、フラミンガムスコア(低リスク3例、中等度5例、高リスク7例)、吹田スコア(低リスク13例、中等度1例、高リスク1例)。1,000人年当たりのIHDおよびCI発症率は、登録されたCML-CP患者でそれぞれ5.26および2.92、イマチニブ治療患者で4.65および2.33、ニロチニブ治療患者で14.34および10.75、ダサチニブ治療患者で4.08および症例なし、年齢をマッチさせた一般集団で1.787および3.342であった。新たにCML-CPと診断された320例のうち、調査期間中に16例(5.0%)のVAEが報告された。イマチニブによる治療が7例、ニロチニブによる治療が3例、ダサチニブによる治療が1例、イマチニブからニロチニブへの切り替えが4例、ダサチニブからニロチニブへの切り替えが1例であった。VAEはIHDが9例、CIが5例、PAODが2例であった。3つのリスク評価ツールの結果は以下の通りである: SCORE(低リスク2例、中等度9例、高リスク1例、超高リスク4例)、フラミンガムスコア(低リスク3例、中等度5例、高リスク7例)、吹田スコア(低リスク13例、中等度1例、高リスク1例)。1,000人年当たりのIHDおよびCI発症率は、それぞれ登録CMLCP患者で5.26および2.92、イマチニブ治療患者で4.65および2.33、ニロチニブ治療患者で14.34および10.75、ダサチニブ治療患者で4.08および症例なし、年齢をマッチさせた一般集団で1.787および3.342であった。
[要約/結論】1000人年当たりのIHD発症率は、ニロチニブ治療CML患者で高く、イマチニブ治療CML患者とダサチニブ治療CML患者で低く、年齢をマッチさせた一般集団と比較してCI発症率はほぼ同じであった。SCOREおよびフラミンガムリスクスコア評価ツールでは、VAEのリスクが非常に高い患者および高い患者が、吹田スコア評価ツールと比較して多かった。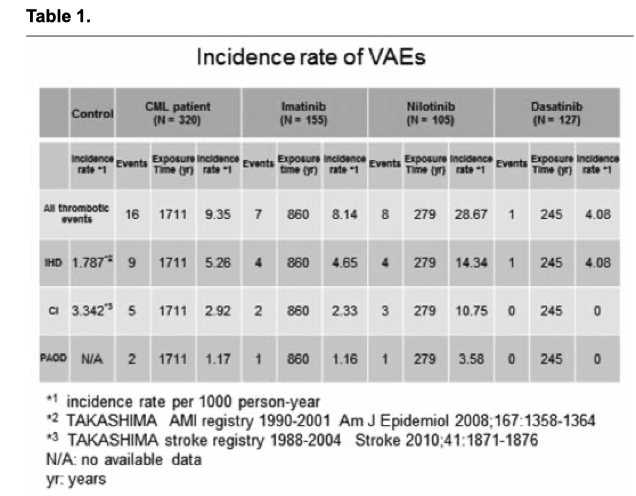
★ E1066
THE INTRODUCTION OF SECOND-GENERATION TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITORS MAY REDUCE THE PROGNOSTIC IMPACT OF HIGH-RISK PATIENTS ACCORDING TO EUROPEAN TREATMENT AND OUTCOME STUDY (EUTOS) SCORE
○E. Sato, N. Iriyama, M. Tokuhira, T. Takaku, M. Ishikawa , T. Nakazato, K.-J. Sugimoto, H. Fujita, I. Fujioka, Y. Hatta, M. Kizaki, N. Komatsu, N. Asou, T. Kawaguchi.
[Background] The discovery of tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) imatinib has revolutionized the conception of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) as a mortal disease to a long-term controllable disease. The European Treatment and Outcome Study (EUTOS) score is a clinical tool that utilizes imatinib-based objectives to predict treatment response and progression free survival (PFS) in patients with CML in chronic phase (CP). However, it is currently unknown whether the introduction of second generation TKIs (2 nd TKIs) affects prognostic score of patients with CML-CP, particularly among those considered high-risk according to EUTOS score.
[Aims] Our study aims to highlight the critical role of the introduction of 2 nd TKIs on patient prognosis as determined by EUTOS score.
[Methods] Patients data was obtained retrospectively from patients enrolled in the CML Cooperative Study Group. Patients with CML-CP who were treated with any TKIs as first line therapy between April 2001 and January 2016 were enrolled to the study and were classified according to date of diagnosis. Those who were diagnosed with CML-CP before March 2009 were classified into the imatinib group, and those diagnosed after April 2009 were classified into the 2 nd TKI group, as these patients were able to be treated with 2 nd TKIs. The study was approved by the research ethics boards of each institution and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
[Results] There were 308 patients newly diagnosed with CML-CP during the study period. Of these patients, 104 (34%) were assigned to the imatinib group and 204 (67%) were assigned to the 2 nd TKI group. With respect to EUTOS score, 223 patients were classified as low-risk, of which 69 were in the imatinib group and 154 were in the 2 nd TKI group. Forty-six patients were considered high-risk, of which 19 were in the imatinib group and 27 were in the 2 nd TKI group. EUTOS score was unavailable in 39 patients. With regard to initial TKI, all patients were treated with imatinib in the imatinib group. Among patients assigned to the 2 nd TKI group, 149 (73%) were initially treated with any TKI. The median follow-up period for all patients was 48 months (range: 1–185 months). Among patients in the 2 nd TKI group, CML-associated death rates were significantly lower than those in the imatinib group. EUTOS high-risk patients score exhibited significantly worse outcomes in EFS, PFS, and CMLassociated death compared to those considered low-risk. Most importantly, risk stratification by EUTOS score was predictive of risk-associated clinical outcomes in patients assigned to the imatinib group; however, EUTOS score failed to predict risk-associated clinical outcomes of patients assigned to the 2 nd TKI group (see Figure). The EUTOS high-risk patients in the imatinib group showed worse clinical outcomes than those in the 2 nd TKI group (hazard ratio [HR] 6.35, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.79 – 22.6, p=0.0042). However, prognostic effect was less in the 2 nd TKI group (HR 3.21, 95% CI 0.59 – 17.6, p=0.18). Out of 308 patients, 9 progressed to AP/BP, of which 8 transformed during imatinib therapy and 1 transformed during dasatinib therapy.
[背景] チロシンキナーゼ阻害剤(TKI)であるイマチニブの発見により、慢性骨髄性白血病(CML)は、死に至る病という概念から、長期的にコントロール可能な病という概念に一変した。European Treatment and Outcome Study(EUTOS)スコアは、慢性期(CP)のCML患者における治療反応性と無増悪生存期間(PFS)を予測するために、イマチニブに基づく目標を利用した臨床ツールである。しかし、第二世代TKI(2nd TKI)の導入がCML-CP患者、特にEUTOSスコアにより高リスクとみなされる患者の予後スコアに影響を及ぼすかどうかは、現在のところ不明である。
[目的] 本研究の目的は、第2世代TKIの導入がEUTOSスコアによって決定される患者の予後に及ぼす重要な役割を明らかにすることである。
方法 CML Cooperative Study Groupに登録された患者からレトロスペクティブに患者データを入手した。2001年4月から2016年1月までの間に第一選択療法としていずれかのTKIが投与されたCML-CP患者が登録され、診断日により分類された。2009年3月以前にCML-CPと診断された患者はイマチニブ群に分類され、2009年4月以降に診断された患者は2nd TKIによる治療が可能であったため2nd TKI群に分類された。本研究は、各施設の研究倫理委員会の承認を受け、ヘルシンキ宣言に従って実施された。
[結果] 研究期間中に新たにCML-CPと診断された患者は308人であった。このうち104例(34%)がイマチニブ群に、204例(67%)が2nd TKI群に割り付けられた。EUTOSスコアに関して、223例が低リスクに分類され、そのうち69例がイマチニブ群、154例が2nd TKI群であった。高リスクとされたのは46例で、そのうちイマチニブ群19例、2nd TKI群27例であった。EUTOSスコアが得られなかった患者は39例であった。初回TKIに関しては、イマチニブ群では全例がイマチニブで治療された。2ndTKI群に割り付けられた患者のうち、149例(73%)がいずれかのTKIで初回治療を受けた。全患者の追跡期間中央値は48ヵ月(範囲:1-185ヵ月)であった。2ndTKI群の患者では、CMLに関連した死亡率はイマチニブ群より有意に低かった。EUTOS高リスク群では、低リスク群に比べ、EFS、PFS、CML関連死が有意に不良であった。最も重要なことは、EUTOSスコアによるリスク層別化は、イマチニブ群に割り付けられた患者のリスク関連臨床転帰を予測したことである。しかし、EUTOSスコアは2nd TKI群に割り付けられた患者のリスク関連臨床転帰を予測できなかった(図参照)。イマチニブ群のEUTOS高リスク患者は、2nd TKI群の患者よりも悪い臨床転帰を示した(ハザード比[HR]6.35、95%信頼区間[CI]1.79-22.6、p=0.0042)。しかし、2nd TKI群では予後への影響は少なかった(HR 3.21, 95% CI 0.59 – 17.6, p=0.18)。308例中9例がAP/BPに進行し、うち8例がイマチニブ治療中に、1例がダサチニブ治療中に進行した。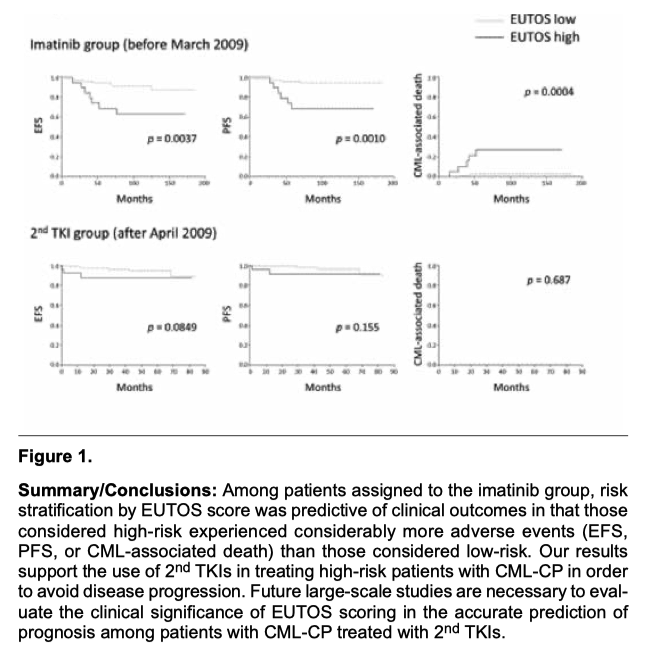
———————————————————————————————————————————————-
☆ American Society of Hematology (ASH) 2016 Annual Meeting (2016/12/03-06) 図説1演題
★ #3084
Clinical Entity and Outcomes of Therapy-Related Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in the Era of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Surveillance By the Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cooperative Study Group.
○Noriyoshi Iriyama, Tomoiku Takaku, Eriko Sato, Maho Ishikawa, Tomonori Nakazato, Kei-Ji Sugimoto, Hiroyuki Fujita, Michihide Tokuhira, Tatsuya Kawaguchi.
[Background and Aim] Therapy-related chronic myeloid leukemia (TR-CML), which is defined as CML that developed after exposure to cytotoxic chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy, rarely exists in clinical practice, although its incidence rates are relatively lower than those of acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndromes, accounting for 1.2-30.4% of secondary leukemias. The clinical behavior of TR-CML, including patient outcome, is reportedly not different from that of de novo CML before the era of imatinib treatment. While the recent advancement of CML treatment by the introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) has dramatically improved treatment outcomes in patients with CML, little is known about the treatment response and outcomes in patients with TR-CML treated with TKI. In this regard, we investigated the clinical entity of TR-CML in the era of TKIs, including treatment response to TKI and prognosis, in patients enrolled to the CML Cooperative Study Group.
[Patients and Methods] We retrospectively reviewed the data of patients enrolled in the CML Cooperative Study to identify patients diagnosed with TR-CML. This study included patients aged >15 years who were diagnosed with CML in the chronic phase between April 2001 and January 2016, and treated with any TKIs as initial therapy and followed up for at least 3 months. The study was approved by the research ethics board of each institution and conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. A major molecular response (MMR) was defined as ≤0.1% on the International Scale (IS) or 100 copies of the BCR-ABL1 transcript/μg RNA in a transcription-mediated amplification and hybridization protection assay. A deep molecular response (DMR) was defined ≤0.0032% in the IS. Event-free survival (EFS) was defined as the period from the date of initial treatment with TKI to the date of onset of the first adverse event (loss of treatment efficacy, progression to the accelerated or blastic phase, or any cause of death) or the last follow-up. Statistical analyses were performed by using EZR.
[Results and Discussion] We identified 308 patients with newly diagnosed CML in the chronic phase, including 11 (3.6%) with TR-CML and 297 with de novo CML. Regarding the primary cancer, 2 of the 11 patients had breast cancer and the remaining 9 had prostate cancer, pharyngeal cancer, mesothelioma, lung cancer, colon cancer, ureter cancer, acute leukemia, gastric cancer, or bladder cancer, respectively. Eight cases were treated with chemotherapy, 2 were treated with radiotherapy, and the remaining case was treated with both chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The results of a cytogenetic analysis by G-banding were exclusive t(9;22)(q34;q11) in all the patients. The median time to diagnosis of CML from the initiation of chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy was 7 years (range, 1.2-33 years). No significant differences in patient age, sex, white blood cell count, hemoglobin level, platelet count, or European Treatment and Outcome Study risk were observed between the TR-CML and de novo CML groups. Among the patients whose cytogenetic and/or molecular responses were assessable, all had excellent treatment response to TKI. Seven patients unexpectedly reached MMR within 6 months after TKI initiation. Finally, 8 patients attained DMR or undetectable leukemia in the bone marrow and the remaining 3 attained MMR. The 5-year EFS of the patients in the de novo CML group was 90%. None of the patients in the TR-CML group experienced any adverse event. In conclusion, in the present study, we revealed that patients with TR-CML could attain a good clinical course with TKI therapy. Detailed investigations of TR-CML may provide new insights into the CML biology.
[背景と目的] 治療関連慢性骨髄性白血病(TR-CML)は、細胞毒性化学療法および/または放射線療法を受けた後に発症したCMLと定義されるが、その罹患率は急性骨髄性白血病や骨髄異形成症候群よりも比較的低く、二次性白血病の1.2〜30.4%を占めるものの、臨床の現場ではほとんど存在しない。患者の転帰を含むTR-CMLの臨床的挙動は、イマチニブ治療時代以前のde novo CMLと変わらないと報告されている。近年、チロシンキナーゼ阻害薬(TKI)の導入によるCML治療の進歩により、CML患者の治療成績は劇的に改善したが、TKI治療を受けたTR-CML患者の治療反応性と転帰についてはほとんど知られていない。この観点から、我々はCML Cooperative Study Groupに登録された患者を対象に、TKIに対する治療反応性や予後など、TKI時代のTR-CMLの臨床的実体について調査した。
[患者と方法] TR-CMLと診断された患者を特定するために、CML Cooperative Studyに登録された患者のデータをレトロスペクティブにレビューした。本研究では、2001年4月~2016年1月の間に慢性期のCMLと診断され、初回治療としていずれかのTKIによる治療を受け、少なくとも3ヵ月間フォローアップされた15歳以上の患者を対象とした。本研究は、各施設の研究倫理委員会の承認を受け、ヘルシンキ宣言に従って実施された。主要分子反応(MMR)は、国際スケール(IS)で0.1%以下、または転写媒介増幅およびハイブリダイゼーション保護アッセイでBCR-ABL1転写物/μg RNAが100コピー以下と定義された。深部分子反応(DMR)はISで0.0032%以下と定義された。無イベント生存期間(EFS)は、TKIによる初回治療日から最初の有害事象(治療効果の消失、促進期または芽球性期への進行、または死因)の発現日、または最終追跡調査日までの期間と定義した。統計解析はEZRを用いて行った。
[結果と考察] 新たに慢性期のCMLと診断された患者308例(TR-CML 11例(3.6%)、de novo CML 297例)を同定した。原発がんについては、11例中2例が乳がんであり、残りの9例はそれぞれ前立腺がん、咽頭がん、中皮腫、肺がん、大腸がん、尿管がん、急性白血病、胃がん、膀胱がんであった。8例は化学療法、2例は放射線療法、残りの1例は化学療法と放射線療法の両方が行われた。Gバンド法による細胞遺伝学的解析の結果、全例でt(9;22)(q34;q11)が認められた。化学療法および/または放射線療法の開始からCMLと診断されるまでの期間の中央値は7年(範囲、1.2-33年)であった。患者の年齢、性別、白血球数、ヘモグロビン値、血小板数、European Treatment and Outcome StudyのリスクにTR-CML群とde novo CML群の間に有意差は認められなかった。細胞遺伝学的および/または分子学的反応が評価可能であった患者のうち、全例がTKIに対して優れた治療反応を示した。7人の患者が予期せずTKI開始後6ヵ月以内にMMRに達した。最終的に、8人の患者がDMRまたは骨髄で検出されない白血病を達成し、残りの3人がMMRを達成した。de novo CML群の患者の5年EFSは90%であった。TR-CML群では、いずれの患者にも有害事象は認められなかった。結論として、TR-CML患者はTKI治療により良好な臨床経過を得ることができた。TR-CMLの詳細な検討により、CMLの生物学に関する新たな知見が得られる可能性がある。
